Content Management API
[API VERSION : 3.0.0]Introduction
Base URL
- US (North America, or NA): https://api.contentstack.io/
- Europe (EU): https://eu-api.contentstack.com/
- Azure North America (Azure NA): https://azure-na-api.contentstack.com/
- Azure Europe (Azure EU): https://azure-eu-api.contentstack.com/
Overview
Contentstack is a headless, API-first content management system (CMS) that provides everything you need to power your web or mobile properties. To learn more about Contentstack, visit our website or refer to our documentation site to understand what we do.
This document is a detailed reference to Contentstack’s Content Management API.
The Content Management API (CMA) is used to manage the content of your Contentstack account. This includes creating, updating, deleting, and fetching content of your account. To use the Content Management API, you will need to authenticate yourself with a Management Token or an Authtoken. Read more about it in Authentication.
Note: The Content Management APIs also include many GET requests. However, it is highly recommended that you always use the Content Delivery API to deliver content to your web or mobile properties.
Content Management SDKs
We have created SDKs, API references, getting started guides, and sample apps for some of the popular languages and platforms. You can use them to build your own apps and manage your content from Contentstack.
Contentstack Management SDKs interact with the Content Management APIs and allow you to create, update, delete, and fetch content from your Contentstack account. They are read-write in nature.
You will find a list of all the available management SDKs under the Content Management SDKs section.
We provide Management SDKs for the following platform:
Authentication
Contentstack provides token-based authentication that allows you to create, update, delete, and fetch the content of your Contentstack account. You can use either the stack’s Management Token, OAuth Token, or the user Authtoken, along with the stack API key, to make Content Management API requests. The API key is a unique key assigned to each stack.
Management Tokens are stack-level read-write tokens that allow making CMA requests without the need to provide user credentials. The Contentstack OAuth server generates access tokens (both App and User tokens), which client applications can employ to retrieve restricted data on behalf of the resource owner. However, Authtokens are user-specific tokens generated when user logs in to Contentstack. Read more about the different types of tokens.
For API Key and Authtoken-based authentication
- Pass the stack’s API key against the api_key parameter as header
- Pass the user Authtoken against the authtoken parameter as header
For API Key and Management Token-based authentication
- Pass the stack’s API key against the api_key parameter as header
- Pass the user Management Token value against the authorization parameter as header
For API Key and OAuth Token-based authentication
- Pass the stack’s API key against the api_key parameter as header for stack based APIs
Pass the OAuth Token value against the authorization parameter as header
Authtokens vs Management Tokens vs OAuth Token
An Authtoken is a read-write token used to make authorized CMA requests, and it is a user-specific token. This means that your personal user details are attached to every API request that you make using the authtoken. So, if a person were to obtain access to your authtoken, and knows the Stack API key, this person would be able to make API requests that appeared to be coming from you.
Management Tokens, on the other hand, are stack-level tokens, with no users attached to them. They can do everything that authtokens can do. Since they are not personal tokens, no role-specific permissions are applicable to them. It is recommended to use these tokens for automation scripts, third-party app integrations, and for Single Sign On (SSO)-enabled organizations.
Contentstack OAuth employs the OAuth 2.0 protocol, enabling external applications to access Contentstack APIs on behalf of users. It issues access tokens (App & User tokens) to client applications, allowing them to retrieve restricted data from the Contentstack resource server without the need for the resource owner to share their credentials. Learn more about Contentstack OAuth and OAuth Scopes.
Authtoken lets you make almost all the Content Management requests, while with Management Tokens, you have a few limitations. For more information, read our Limitations of Management Tokens documentation.
Note: When trying out POST/PUT calls, in addition to the API Key and Authtoken / Management token, you need to mandatorily pass Content-Type:application/json in the Header.
How to Get Stack API Key
To retrieve the stack API key, perform the steps given below:
- Go to your stack.
- Navigate to Settings > Stack.
- On the right-hand side of the page, under API CREDENTIALS, you will get the API Key of your stack.
Note: Only the developers, admins and stack owners can view the API key.
How to Get Authtoken
To retrieve the authtoken, log in to your Contentstack account by using the "Log in to your account" request under "User Session". This request will return the authtoken in the response body.
You can generate multiple authtokens by executing the "Log in to your account" request multiple times. These tokens do not have an expiration time limit. However, currently, there is a maximum limit of 20 valid tokens that a user can use per account at a time, to execute CMA requests. If you already have valid 20 tokens, creating a new authtoken will automatically cause the oldest authtoken to expire without warning.
For SSO-enabled organizations, the "Log in to your account" request will not return the user authtoken for users who access the organization through Identity Provider login credentials. Consequently, any requests that require user authtoken will not work. Only the owner of the organization and users with permission to access the organization without SSO can use the Content Management APIs. Learn more about REST API Usage.
How to Get Management Tokens
To get the Management Token, perform the steps given below after logging into your Contentstack account:
- Go to your stack.
- Navigate to Settings > Tokens > Management Tokens.
- From the list, pick the Management Token that you want.
Read more about how you can create a new Management Token.
Note: Only the stack Owner and Admin users can create Management Tokens.
You can generate multiple management tokens for a specific stack within your organization. However, there is a maximum limit of 10 valid tokens that can exist per stack at a time, to execute CMA requests. If you already have 10 valid tokens, creating a new management token will automatically cause the oldest management token to expire without warning.
How to Get OAuth Tokens
To get the OAuth Token, perform the steps given within the Configuring Contentstack OAuth section after logging into your Contentstack account.
Note: Only the organization Owner and Admin users can create OAuth Tokens.
Rate limiting
Rate limit is the maximum number of requests you can make using Contentstack’s API in a given time period.
By default, the Contentstack Management API enforces the following rate limits:
- Read (GET) requests: 10 requests per second per organization.
- Write (POST/PUT/DELETE) requests: 10 requests per second per organization.
Your application will receive the HTTP 429 response code if the requests for a given time period exceed the defined rate limits.
Note: Bulk actions do not follow the standard CMA rate limit of 10 requests per second. The default rate limit for bulk actions is 1 request per second i.e., in one second you can make only one bulk publish API request.
We also have set a limit on stack creation. Organizations can create only one stack per minute.
The aforementioned limits are configurable depending on your plan. For more information, contact our Support team.
To get the current rate limit status, you can check the returned HTTP headers of any API request. These rate limits are reset at the start of each time period.
| Headers | Description |
|---|---|
| X-RateLimit-Limit | The maximum number of request a client is allowed to make per second per organization. |
| X-RateLimit-Remaining | The number of requests remaining in the current time period. |
API conventions
- The base URL for Content Management API for different regions can be found in the Base URL section.
- The API version (in our case, 'v3') can be found in the URL, e.g. api.contentstack.io/v3/endpoint.
- Content Management API supports GET/POST/PUT/DELETE verbs or methods.
- URL paths are written in lower case.
- Query parameters and JSON fields use lower case, with underscores (_) separating words.
- The success/failure status of an operation is determined by the HTTP status it returns. Additional information is included in the HTTP response body.
- The JSON number type is bounded to a signed 32-bit integer.
Errors
If there is something wrong with the API request, Contentstack returns an error.
Contentstack uses conventional, standard HTTP status codes for errors, and returns a JSON body containing details about the error. In general, codes in the 2xx range signify success. The codes in the 4xx range indicate error, mainly due to information provided (for example, a required parameter or field was omitted). Lastly, codes in the 5xx range mean that there is something wrong with Contentstack’s servers; it is very rare though.
Let’s look at the error code and their meanings.
| HTTP status code | Description |
|---|---|
| 400 Bad Request | The request was incorrect or corrupted. |
| 401 Access Denied | The login credentials are invalid. |
| 403 Forbidden Error | The page or resource that is being accessed is forbidden. |
| 404 Not Found | The requested page or resource could not be found. |
| 412 Pre Condition Failed | The entered API key is invalid. |
| 422* Unprocessable Entity (also includes Validation Error and Unknown Field) | The request is syntactically correct but contains semantic errors. |
| 429 Rate Limit Exceeded | The number of requests exceeds the allowed limit for the given time period. |
| 500 Internal Server Error | The server is malfunctioning and is not specific on what the problem is. |
| 502 Bad Gateway Error | A server received an invalid response from another server. |
| 504 Gateway Timeout Error | A server did not receive a timely response from another server that it was accessing while attempting to load the web page or fill another request by the browser. |
* Contentstack returns the 422 HTTP status code for an error along with the "UID is not valid" message in the response body either when an entry doesn’t exist within the stack, has been deleted from the content type, or exists within a different content type. As the entry has been deleted or unpublished, the Content Delivery Network (CDN) cannot identify the specified entry UID through the cache servers. To check whether the entry has been deleted, try retrieving the entry from CDN first. If the API request fails to retrieve the entry from CDN, then make an API request to the Origin server to check whether the entry exists.
Note: The error codes that we get in the JSON response are not HTTP error codes but are custom Contentstack error codes that are used for internal purposes.
Using Postman Collection
Contentstack offers you a Postman Collection that helps you try out our Content Management API. You can download this collection, connect to your Contentstack account, and try out the Content Management API with ease.
Learn more about how to get started with using the Postman Collection for Contenstack Content Management API.
Using OpenAPI Files
Contentstack provides the OpenAPI files of the Contentstack’s Content Management APIs (CMA) that you can use to try out Contentstack APIs on any OpenAPI platform such as Swagger. You can download the OpenAPI JSON file of the Content Management API and open it on Swagger Editor to start using it.
Learn more about how to get started with using the OpenAPI files for Contenstack Content Management API.
API Reference
User Session
User session consists of calls that will help you to sign in and sign out of your Contentstack account.
Logging in/out
The Log in to your account request is used to sign in to your Contentstack account and obtain the authtoken.
Note: The authtoken is a mandatory parameter when executing Content Management API calls. However, when executing Content Delivery API calls, use the Content Delivery base URL for your region, and pass the environment-specific delivery token against the access_token key.
In the 'Body' section, enter the user credentials in JSON format. The JSON query will include the email address, the Contentstack user account password, and the two-factor authentication token (if enabled) received in the Authy app or SMS.
For SSO-enabled organizations, the ‘Log in to your account’ request will not return the user authtoken for users. In this case, you can try out the following:
- The owner of an organization can access the SSO-enabled organization through Contentstack credentials and retrieve the user authtoken to make Content Management API requests.
- Disable 'Strict Mode' for an SSO-enabled organization, and users who have the ability to access their organization through Contentstack credentials can retrieve the authtoken to make Content Management API requests.
For more details, refer the REST API Usage - Content Management API section in the Single Sign-On page.
The Log out of your account call is used to sign out the user of Contentstack account.
Users
All accounts registered with Contentstack are known as Users. A stack can have many users with varying permissions and roles.
Note: Before executing any calls, retrieve the authtoken by authenticating yourself via the Log in call of User Session. The authtoken is returned in the 'Response' body of the Log in call and is mandatory in all of the calls. Example: blt3cecf75b33bb2ebe
Get User
The Get user call returns comprehensive information of an existing user account. The information returned includes details of the stacks owned by and shared with the specified user account.
Update User
The Update User API Request updates the details of an existing user account. Only the information entered here will be updated, the existing data will remain unaffected.
When executing the API call, under the 'Body' section, enter the information of the user that you wish to update. This information should be in JSON format.
Additional Resource: To update the role of an existing user, refer to the Update Existing User Role API Request.
Activate User
The Activate a user account call activates the account of a user after signing up. For account activation, you will require the token received in the activation email.
Request Password
The Request for a password API helps to get a temporary password to log into an account in case a user has forgotten the login password.
Using this temporary password, you can log in to your account and set a new password for your Contentstack account.
In the 'Body' section, provide the user's email address in JSON format.
Note: The “Reset password” token that you receive in your email address is valid only for the next 60 minutes after it’s generated. Post that, it expires and you need to rerun the Reset password API request to generate a new token.
Reset Password
The Reset password API request allows you to reset your Contentstack account password.
Note: Before using this API request, you need to execute the Request for a password API request to receive the reset password token in your registered email address.
When executing the request, in the 'Body' section, you need to provide the token that you receive via email, your new password, and password confirmation in JSON format.
Note: The "Reset password" token is valid only for the next 60 minutes after it’s generated. Post that, it expires and you need to rerun the same request to generate a new token.
Organizations
Organization is the top-level entity in the hierarchy of Contentstack, consisting of stacks and stack resources, and users. Organization allows easy management of projects as well as users within the Organization.
Get All Organizations
The Get all organizations call lists all organizations related to the system user in the order that they were created.
Get Single Organization
The Get a single organization call gets the comprehensive details of a specific organization related to the system user.
Organization Roles
The Get all roles in an organization call gives the details of all the roles that are set to users in an Organization.
When executing the API call, provide the Organization's UID.
Organization Users
The Get Organization users by email request retrieves information about users within an organization based on their email addresses.
When executing the API request, you need to provide the organization UID. In the request body, you need to enter the email IDs of the users whose details you want to retrieve from the mentioned organization, like as follows:
{
"emails":["abc@sample.com", "xyz@sample.com", …]
}
Note: If you do not pass the request body, you will get the details of all the users in the Organization.
The Add users to organization request allows you to send invitations to add users to your organization. Only the owner or the admin of the organization can add users.
When executing the API request, in the request body, provide the organization admin/member role ID, obtained from the Get all roles in an Organization request. Also, provide the stack role UID of the user in the request body, obtained from the Get all roles request.
The Remove users from organization request allows you to remove existing users from your organization.
Note: Only the owner or the admin of the organization can remove users.
When executing the API request, provide the organization UID. In the “Body” section, you need to enter the email IDs of the users you want to remove from the organization as follows:
{
"emails":[
"abc@sample.com", "xyz@sample.com"
]
}
The Resend pending organization invitation request allows you to resend the Organization invitations to users who have not yet accepted the earlier invitation. Only the owner or the admin of the Organization can resend the invitation to add users to an Organization.
When executing Get all organization invitations request, you get the invitation status that helps to identify the pending invitations and share UID. When executing the Resend pending organization invitation API request, provide the Organization UID and share UID.
The Get all organization invitations call gives you a list of all the Organization invitations. Only the owner or the admin of the Organization can resend the invitation to add users to an Organization.
When executing the API call, provide the Organization UID.
Transfer Organization Ownership
The Transfer organization ownership call transfers the ownership of an Organization to another user. When the call is executed, an email invitation for accepting the ownership of a particular Organization is sent to the specified user.
Once the specified user accepts the invitation by clicking on the link provided in the email, the ownership of the Organization gets transferred to the new user. Subsequently, the previous owner will no longer have any permission on the Organization.
When executing the API call, provide the Organization UID.
Organization Stacks
The Get all stacks in an organization call fetches the list of all stacks in an Organization.
When executing the API call, provide the Organization UID.
Organization Logs
The Get organization log details request is used to retrieve the audit log details of an organization.
You can apply queries to filter the results. Refer to the Queries section for more details.
Tip: This request returns only the first 25 audit log items of the specified organization. If you get more than 25 items in your response, refer the Pagination section to retrieve all the log items in paginated form.
The Get organization log item request is used to retrieve a specific item from the audit log of an organization.
TeamsNEW
Teams, simplifies role and permission management by grouping users. Instead of assigning roles individually or at the stack level, you can directly assign roles to a team. This ensures that all team members share the same set of role permissions.
Get all teams
The Get all teams request returns comprehensive information of all the teams available in your organization.
Get a single team
The Get a single team request returns comprehensive information of a specific team available in a particular organization.
Create a team
The Create a team request creates a team in the specified organization.
Update a team
The Update a team request is used to modify details, such as adding or removing users from a team, assigning or removing stack roles within a team, updating team descriptions, and updating organization roles for an existing team within a specific organization.
Delete a team
The Delete a team request deletes an existing team along with all its associated users and assigned roles.
Users
All accounts registered with Contentstack are known as Users. An organization can have many users with varying permissions and roles.
Get all users of team
The Get all users of team request retrieves information about all the users associated with a particular team.
Add users to team
The Add users to team request allows you to send invitations to add users and assign them organizational and stack roles.
Note: Only the Owner or the Admin of the organization can add users to a team.
You need to pass the email IDs of the users in the request body as follows:
{
"emails": [ "user1@contentstack.com", "user2@contentstack.com"]
}
Remove a user from team
The Remove a user from team request allows you to remove an existing user from a particular team.
Note: Only the Owner or the Admin of the organization can remove users from a team.
Stack Role Mapping
When adding users to a team, you have the option to simultaneously assign roles for the available stacks within the organization. This process involves mapping stack roles for all the users added to the team.
Get all stack role mapping
The Get all stack role mapping request allows you to retrieve details of all associated stacks for a specified team in your organization.
Add a stack role mapping
The Add a stack role mapping request allows you to associate users from a specified team with the available stacks in your organization.
You need to pass the API key of the stack and the role UIDs in the request body as follows:
{
"stackApiKey": "stack_api_key",
"roles": [
"role_one_uid",
"role_two_uid"
]
}
Update a stack role mapping
The Update a stack role mapping request allows you to update the stack roles for a specific stack in your organization. You need to pass the role UIDs in the request body as follows:
{
"roles": [
"role_uid"
]
}
Remove a stack role mapping
The Remove a stack role mapping request allows you to delete the associations of team users for a specified stack in your organization.
Stacks
A stack is a space that stores the content of a project (a web or mobile property). Within a stack, you can create content structures, content entries, users, etc. related to the project.
Get Single Stack
The Get a single stack call fetches comprehensive details of a specific stack.
Note: For SSO-enabled organizations, it is mandatory to pass the organization UID in the header.
Get All Stacks
The Get all stacks call fetches the list of all stacks owned by and shared with a particular user account.
Note: For SSO-enabled organizations, it is mandatory to pass the organization UID in the header.
Create Stack
The Create stack call creates a new stack in your Contentstack account.
In the 'Body' section, provide the schema of the stack in JSON format.
Note: At any given point of time, an organization can create only one stack per minute.
Update Stack
The Update stack call lets you update the name and description of an existing stack.
In the 'Body' section, provide the updated schema of the stack in JSON format.
Warning: The master locale cannot be changed once it is set while stack creation. So, you cannot use this call to change/update the master language.
Delete stack
The Delete stack call is used to delete an existing stack permanently from your Contentstack account.
Get all users
The Get all users of a stack call fetches the list of all users of a particular stack
Update Existing User Role
The Update User Role API Request updates the roles of an existing user account. This API Request will override the existing roles assigned to a user. For example, we have an existing user with the "Developer" role, and if you execute this API request with "Content Manager" role, the user role will lose "Developer" rights and the user role be updated to just "Content Manager".
When executing the API call, under the 'Body' section, enter the user UID and UIDs of roles that you want to assign the user. This information should be in JSON format.
Transfer Stack Ownership
The Transfer stack ownership to other users call sends the specified user an email invitation for accepting the ownership of a particular stack.
Once the specified user accepts the invitation by clicking on the link provided in the email, the ownership of the stack gets transferred to the new user. Subsequently, the previous owner will no longer have any permission on the stack.
In the 'Body' section, you need to provide the email address of the user to whom you wish to transfer the ownership of the stack in JSON format.
Additional Resource: To transfer ownership of a stack to other users via Contentstack's UI, refer to the Transfer Stack Ownership article.
Accept Stack Ownership
The Accept stack owned by other user call allows a user to accept the ownership of a particular stack via an email invitation.
The email invitation includes a link (i.e., /stack/accept_ownership/{ownership_token}?api_key={api_key}&uid={user_uid} ) that consists of the ownership token, the API key, and user uid.
Once the user accepts the invitation by clicking on the link, the ownership is transferred to the new user account. Subsequently, the user who transferred the stack will no longer have any permission on the stack.
When executing the API call, in the 'URL Parameters' section, you need to provide the ownership token and the user uid that you received in the invitation mail.
Stack Settings
The Get stack settings call retrieves the configuration settings of an existing stack.
The Add stack settings request lets you add additional settings for your existing stack.
You can add specific settings for your stack by passing any of the following parameters within the stack_variables section in the “Request Body”:
- "enforce_unique_urls": true: Ensures that entry URLs are not duplicated across the stack.
- "sys_rte_allowed_tags": "figure, style, script": You can pass a combination of the three values, figure, style, and script, to this parameter (e.g., "sys_rte_allowed_tags": "figure, style, script", "sys_rte_allowed_tags": "figure", etc.):
- figure: Wraps images inside the “Rich Text Editor” field within the <figure> tag.
- style: Allows to use the <style> tag within the HTML code of a “Rich Text Editor” field.
- script: Allows to use the <script> tag within the HTML code of a “Rich Text Editor” field.
Note: Contentstack highly recommends that you avoid using the <script> tag within the HTML code of a “Rich Text Editor” field due to its security vulnerabilities.
- "sys_rte_skip_format_on_paste": "GD:font-size": Skips the font-size attribute, and GD indicates the external vendor Google Document’s prefix.
- "sys_rte_skip_format_on_paste":"GD:color": Skips the color attribute, and GD indicates the external vendor Google Document’s prefix.
- "sys_rte_skip_format_on_paste":"GD:background-color": Skips the background-color attribute, and GD indicates the external vendor Google Document’s prefix.
- "sys_rte_skip_format_on_paste": "MW:color": Skips the color attribute, and MW indicates the external vendor Microsoft Word’s prefix.
Note: We are currently supporting four attributes (GD:font-size, GD:color, GD:background-color, and MW:color) for this key. This is applicable for both HTML and JSON Rich Text Editors. For more information, refer to the API Change Log for this update.
The editor normally uses the "enter" key for paragraphs and "shift+enter" for line breaks. However, by enabling "cs_only_breakline": true and "cs_breakline_on_enter": true in the "rte" parameter, pressing "enter" creates a line break, and "shift+enter" creates a new paragraph.
Here’s a sample of the Request Body:
{
"stack_settings": {
"stack_variables": {
"enforce_unique_urls": true,
"sys_rte_allowed_tags": "style,figure,script",
"sys_rte_skip_format_on_paste": "GD:font-size","GD:color","GD:background-color","MW:color"
},
"rte": {
"cs_breakline_on_enter": true,
"cs_only_breakline": true
}
}
}
If you exclusively set "cs_only_breakline": true within the "rte" parameter, it ensures that only a <br> tag is inserted in the "Rich Text Editor" field when the content manager presses "Enter". Conversely, when this parameter is set to false, the <br> tag is substituted with <p></p>.
The Reset stack settings call resets your stack to default settings, and additionally, lets you add parameters to or modify the settings of an existing stack.
Share Stack
The Share a stack call shares a stack with the specified user to collaborate on the stack.
In the 'Body' section, you need to provide the email ID of the user with whom you wish to share the stack along with the role uid that you wish to assign the user.
Unshare Stack
The Unshare a stack call unshares a stack with a user and removes the user account from the list of collaborators. Once this call is executed, the user will not be able to view the stack in their account.
In the 'Body' section, you need to provide the email ID of the user from whom you wish to unshare the stack.
Branches
Branches allows you to isolate and easily manage your “in-progress” work from your stable, live work in the production environment. It helps multiple development teams to work in parallel in a more collaborative, organized, and structured manner without impacting each other.
Get All Branches
The Get all branches request returns comprehensive information of all the branches available in a particular stack in your account.
You can add queries to extend the functionality of this API call. Under the 'URL Parameters' section, insert a parameter named query and provide a query in JSON format as the value. (Refer Queries)
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.branches.management:read scope.
Get a Single Branch
The Get a single branch request returns information of a specific branch.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.branches.management:read scope.
Create a Branch
The Create a branch request creates a new branch in a particular stack of your organization.
Note: Only stack owners, admins, and developers can create a new branch. You must only use the authtoken to create a branch.
In the “Body” section, you need to provide a custom UID for the new branch and also the UID of the source branch from which it will inherit data.
Delete a Branch
The Delete a branch request deletes an existing branch and all the content within it.
To confirm the deletion of a branch, you need to specify the force=true query parameter.
Note: You need to delete the child branches before deleting the parent branch. If a branch is the source for any other branch, irrespective of whether you pass a force parameter or not, the API will not allow you to delete that branch.
You must only use the authtoken to delete a branch.
Additional Resource: Deleting a branch also deletes the alias pointing towards it.
When executing the API call, in the “URL Parameters” section, provide the UID of your branch.
Comparing BranchesNEW
With the Comparing Branches functionality, you can compare and check the differences between any two branches.
Compare Branches
The Compare branches request returns a list of all the differences between two branches.
- The compare branches feature is only available for the content types and global fields modules.
- If the number of Content Types/Global Fields that need to be compared is more than 100, you will receive a Next URL in the response body. The comparison limit is set at 100, and for every comparison that goes beyond this limit, the process will be completed in segments of 100.
Compare Content Type between Branches
The Compare content types between branches request returns a list of all the differences in content types between the two specified branches.
Compare Global Fields between Branches
The Compare global fields between branches request returns a list of all the differences in global fields between the two specified branches.
Compare Specific Content Types between Branches
The Compare specific content type between branches request returns all the differences of the specified content type between the two specified branches.
Compare Specific Global Fields between Branches
The Compare specific global field between branches request returns all the differences of the specified global field between the two specified branches.
Merging BranchesNEW
The Merging Branches functionality enables you to merge two branches, integrating the development changes made in the compare branch into the base branch.
Merge Branches
The Merge branches request merges the specified two branches as per the merge strategy selected.
Additional Resource: To learn how to select and use the merge strategies, refer to our documentation on Merging Branches.
You can pass ignore in the default_merge_strategy query parameter, and pass the item_merge_strategies in the request body to override the default strategy and use a different merge strategy for specific content types or global fields.
Here are the details of available merge strategies and what each strategy does:
| Merge Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
merge_prefer_base | Merges the changes from the compare branch into the base branch, keeping the base branch's changes if there are conflicts. |
merge_prefer_compare | Merges the changes from the compare branch into the base branch, keeping the compare branch's changes if there are conflicts. |
overwrite_with_compare | Replaces the base branch with the compare branch, discarding any changes that are not in the compare branch. |
merge_new_only | Adds only new items from the compare branch to the base branch ignoring the modified items. |
merge_modified_only_prefer_base | Merges the modified items from the compare branch into the base branch, keeping the base branch's changes if there are conflicts. |
merge_modified_only_prefer_compare | Merges the modified items from the compare branch into the base branch, keeping the compare branch's changes if there are conflicts. |
ignore | Doesn’t merge the compare branch directly with the base branch. Lets users choose to merge each item from the compare branch into the base branch individually, using the desired merge strategy. |
- The merge branches feature is only available for the content types and global fields modules.
- You can create an additional revert branch beyond the established maximum limit of branches per stack. For instance, if you already have reached the maximum limit of branches in your stack, you can perform a merge operation, provided that you manually delete the backup branch or any other branch before attempting the next merge.
Get all Merge Jobs
The Get all merge jobs request returns a list of all the recent merge jobs within a specific period.
Note: By default, the last 100 merge jobs are returned in the response.
Get a Single Merge Job
The Get single merge job request returns the status and configuration details of a particular merge job.
Aliases
An alias acts as a pointer to a particular branch. You can specify the alias ID in your frontend code to pull content from the target branch associated with an alias.
Get All Aliases
The Get all aliases request returns comprehensive information of all the aliases available in a particular stack in your account.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.branch-aliases.management:read scope.
Get a Single Alias
The Get a single alias request returns information of a specific alias.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.branch-aliases.management:read scope.
Assign an Alias
The Assign an alias request creates a new alias in a particular stack of your organization. This alias can point to any existing branch (target branch) of your stack.
Note: Only stack owners, admins, and developers can assign a new alias to a branch. You must only use the authtoken to assign an alias.
Delete an Alias
The Delete an alias request deletes an existing alias.
To confirm the deletion of an alias, you need to specify the force=true query parameter.
When executing the API call, in the “URL Parameters” section, provide the UID of your alias.
Note: You must only use the authtoken to delete an alias.
Content Types
Content type defines the structure or schema of a page or a section of your web or mobile property. To create content for your application, you are required to first create a content type, and then create entries using the content type.
You can now pass the branch header in the API request to fetch or manage modules located within specific branches of the stack. Additionally, you can also set the include_branch query parameter to true to include the _branch top-level key in the response. This key specifies the unique ID of the branch where the concerned Contentstack module resides.
Additional Resource: To get an idea of building your content type as per webpage’s layout, we recommend you to check out our Content Modeling guide.
Get All Content Types
The Get all content types call returns comprehensive information of all the content types available in a particular stack in your account.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.content-types.management:readscope.
When executing the API call, you can add queries to extend the functionality of this API call.
Tip: If any of your content types contains a Global field and you wish to fetch the content schema of the Global field, then you need to pass the include_global_field_schema:true parameter. This parameter helps return the Global field's schema along with the content type schema.
Under the 'URL Parameters' section, insert a parameter named query and provide a query in JSON format as the value. (To learn more about the queries, refer to the Queries section of the Content Delivery API doc.)
Note: This API request will return a maximum of 100 content types. To retrieve the next batch of content types, make use of the skip parameter (or refer Pagination for more details).
Get Single Content Type
The Get a single content type call returns information of a specific content type.
Enter the version of the content type of which you want to retrieve the details as a query parameter. If no version is specified, you will get the latest version of the content type.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.content-types.management:read scope.
Note: The schema of the content type returned will depend on the provided version. If no version is specified, you will get the latest version of the content type.
To learn more about the queries, refer to the Queries section of the Content Delivery API doc.
Tip: If any of your content types contains a Global field and you wish to fetch the content schema of the Global field, then you need to pass theinclude_global_field_schema:true parameter. This parameter helps return the Global field's schema along with the content type schema.
Create Content TypeNEW
The Create a content type call creates a new content type in a particular stack of your Contentstack account.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.content-types.management:write scope.
In the “Body” section, you need to provide the complete schema of the content type. You can refer the JSON schema for creating a content type document to know how you can add fields into your content type through API.
To mark a field as non-unique, you need to set the unique parameter to false. For example, to remove the unique constraint on the default 'title' field, you need to update the JSON schema of the title field as follows:
{
"display_name": "Title",
"uid": "title",
"data_type": "text",
"mandatory": true,
"unique": false,
"field_metadata": {
"_default": true
},
"multiple": false
}
Create Content Type with Select Field
The Create content type with select field request allows you to add a Select field while creating a content type. You can add choices within the Select field either in the form of single values or key-value pairs.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.content-types.management:write scope.
To add single-value choices, under enum, set the advanced parameter to false and define the choice values under the choices parameter.
The schema of the Select field will look as follows:
"enum":{
"advanced":false,
"choices":[
{
"value":"1"
},
{
"value":"2"
},
{
"value":"3"
}
]
},
To add key-value pairs as choices, under enum, set the advanced parameter to true and define the key-value choices under the choices parameter.
The schema of the Select field that contains key-value pairs will look as follows:
"enum":{
"advanced":true,
"choices":[
{
"key":"New York",
"value":"NY"
},
{
"key":"India",
"value":"IN"
},
{
"key":"Australia",
"value":"AUS"
}
]
},
Additional Resource: In the “Body” section, you need to provide the updated schema of your content type with the select field schema. You can refer to the Select field JSON schema document to know how you can add/update schema for the Select field in your content type through API.
Create Content Type with JSON RTE
The Create content type with JSON RTE request shows you how to add a JSON RTE field while creating a content type.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.content-types.management:write scope.
In the “Body” section, you need to provide the complete schema of the content type with the JSON RTE schema as follows. You can find more details in the JSON schema of the JSON RTE document.
{
"data_type":"json",
"display_name":"JSON RTE",
"uid":"json_rte",
"field_metadata":{
"allow_json_rte":true,
"rich_text_type":"advanced",
"description":"",
"default_value":""
},
"reference_to":[
"content_type_uid"
],
"non_localizable":false,
"multiple":false,
"mandatory":false,
"unique":false
}
Under the reference_to parameter, mention the UIDs of the content types whose entries you wish to embed within the JSON RTE field.
Create content type with custom asset field
The Create content type with custom asset field request is used to create a content type with a custom field that accepts data of type asset.
Create content type with taxonomy
The Create content type with taxonomy request shows you how to add a taxonomy field while creating a content type.
In the “Body” section, you need to provide the complete schema of the content type with the Taxonomy schema as follows:
{
"uid":"taxonomies",
"taxonomies":[
{
"taxonomy_uid":"taxonomy_1",
"max_terms":5,
"mandatory":true,
"non_localizable":false
},
{
"taxonomy_uid":"taxonomy_2",
"max_terms":10,
"mandatory":false,
"non_localizable":false
}
],
"multiple":true
}
Update Content Type
The Update Content Type call is used to update the schema of an existing content type.
Note: Whenever you update a content type, it will auto-increment the content type version.
When executing the API call, in the “URL Parameters” section, provide the uid of your content type.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.content-types.management:write scope.
In the “Body” section, you need to provide the updated schema of your content type. You can refer the JSON schema for creating a content type document to know how you can add/update fields in your content type through API.
Set Field Visibility Rule for Content Type
The Set Field Visibility Rule for Content Type API request lets you add Field Visibility Rules to existing content types. These rules allow you to show and hide fields based on the state or value of certain fields.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.content-types.management:write scope.
Field Visibility Rules can be set while creating your content type (via UI, only after you’ve added all the required fields to the content type and saved it) or while editing a content type (both via UI and API).
To set a Field Visibility Rule, you need to add the following code snippet in the Request body of the content type:
{
...
"content_type": {
"field_rules": [{
"conditions": [{
"operand_field": "operand_field_uid",
"operator": "equals",
"value": "value_corresponding_to_operator"
}],
"match_type": "all",
"actions": [{
"action": "show",
"target_field": "target_field_uid"
}]
}]
}
...
}
Let’s look at the keys used in the above code snippet:
- operand_field: Pass the UID of the Operand field (operand_field_uid) i.e., the field on which you want to set the condition.
- operator: Pass the operator that you want to act on the operand field. Here’s the list of operators that are applicable based on the data type of your operand field:
Data Types Operations Text matches, does_not_match, starts_with, ends_with, contains Number equals, not_equals, less_than, greater_than, less_than_or_equals, greater_than_or_equals Date equals, not_equals, before_date, after_date Boolean is, is_not Select is, is_not Reference is, is_not - value: Pass the value that is corresponding to the operator that you have used. Note that for Date data type, you need to pass the date in ISO format.
- match_type: You need to pass either all or any depending on whether you want all your conditions or any one of your conditions to be met.
- action: You need to pass either show or hide depending on whether you want to show or hide the Target field.
- target_field: Pass the UID of the Target field (target_field_uid) i.e., the field on which you want to perform the action.
For more details, check out the Define Conditions section when adding a Field Visibility Rule.
Delete Content Type
The Delete Content Type call deletes an existing content type and all the entries within it.
When executing the API call, in the “URL Parameters” section, provide the UID of your content type.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.content-types.management:write scope.
Content Type References
The Get all references of content type call will fetch all the content types in which a specified content type is referenced.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.content-type:read scope.
Additionally, to fetch all Global fields in which the specified content type is referenced, you need to pass include_global_fields as a query parameter. Set this parameter to true to include the Global fields along with the content types.
Export Content Type
This call is used to export a specific content type and its schema. The data is exported in JSON format. The exported file won’t get downloaded automatically. To download the exported file, a REST API client, such as Postman can be used.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.content-types:export scope.
However, please note that the entries of the specified content type are not exported through this call.
The schema of the content type returned will depend on the version number provided.
Import Content Type
The Import a content type call imports a content type into a stack by uploading JSON file.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.content-types:import scope.
Tip: You can try the call manually in any REST API client, such as Postman. You can export the required content type's JSON file, make the necessary changes to the data and then import the content type. While importing, you need to pass a form-data parameter named content_type and select the input type as 'File'. Then, select the JSON file of the content type that you wish to import.
TaxonomyNEW
Taxonomy, simplifies the process of organizing content in your system, making it effortless to find and retrieve information. It allows you to arrange your web properties in a hierarchy according to your specific needs, whether it's their purpose, intended audience, or other aspects of your business.
Get all taxonomies
The Get all taxonomies request returns comprehensive information of all the taxonomies available in a particular stack in your organization.
Get a single taxonomy
The Get a single taxonomy request returns comprehensive information of a specific taxonomy available in a particular stack.
Create a taxonomy
The Create a taxonomy request creates a taxonomy in a particular stack of your organization.
Update a taxonomy
The Update a taxonomy request is used to update the details of an existing taxonomy available in a particular stack.
Export a taxonomyNEW
The Export a taxonomy request is used to export a specific taxonomy and its terms. The file is exported in JSON or CSV format. The exported file won’t get downloaded automatically. To download the exported file, a REST API client, such as Postman can be used.
Import a taxonomyNEW
The Import a taxonomy request is used to import a taxonomy and its terms into a stack by uploading the JSON or CSV file.
Note: As Taxonomies can contain numerous terms, the response will feature a terms_count field, indicating the number of successfully imported terms for this request, rather than listing them all.
You can try the call manually in any REST API client, such as Postman. While importing, you need to pass a form-data parameter named taxonomy and select the input type as 'File'. Then, select the JSON or CSV file of the taxonomy that you wish to import.
Note: If the CSV import format is invalid, any invalid rows containing taxonomy/terms and subsequent rows will be ignored. Only rows with valid taxonomy/terms will be created.
Delete a taxonomy
The Delete a taxonomy request deletes an existing taxonomy and all the terms within it. To confirm the deletion of a taxonomy, you need to specify the force=true query parameter.
Note: When you delete a taxonomy, its existing associations with content types are removed. Additionally, the child terms will also eliminate associations with existing entries.
Terms
Terms are the primary classification elements you generate within a taxonomy. They serve the purpose of categorizing entries.
Get all terms of a taxonomy
The Get all terms of a taxonomy request returns comprehensive information of all the terms within a taxonomy available in a particular stack in your organization.
Get a single term
The Get a single term request returns comprehensive information of a specific term available in a particular taxonomy.
Create a term
The Create a term request creates a term in a particular taxonomy within your stack.
Since terms are organized hierarchically in a taxonomy, it's important to define the order when creating new terms. For instance, when creating a term at the parent level, set the parent_uid as null and specify the level within the order parameter. To create a child term, provide the parent_uid of the parent term where you want to add the new child term, and indicate the desired level within the order parameter.
When creating terms at the parent level, the request body should look like this:
{
"term":{
"uid":"term_2",
"name":"Term 2",
"parent_uid":null,
"order":2
}
}
When creating terms at the child level, the request body should look like this:
{
"term":{
"uid":"sub_term_t",
"name":"Sub Term 5",
"parent_uid":"term_1",
"order":5
}
}
Note: The order key signifies the term's position relative to other terms at the same level. The order of terms starts from 1, so to place a term in the first position at that level, set the order as 1.
Update a term
The Update a term request is used to update the details of an existing term available in a particular taxonomy.
Get descendants of a term
The Get descendants of a term request returns all the child terms of a specific term available in a particular taxonomy.
Get ancestors of a term
The Get ancestors of a term returns all the terms that are at higher levels in a specific taxonomy of the specified term.
Move/Reorder a term
The Reorder a term request is used to reposition an existing term available in a particular taxonomy.
The order key signifies the term's position relative to other terms at the same level. The order of terms starts from 1, so to place a term in the first position at that level, set the order as 1.
Note: By default, the force query parameter is set to false, which results in an error if an attempt is made to move a term with child terms. When set to true, it will forcefully move the term, impacting the hierarchy of all its child terms and ancestors.
When reordering terms at the parent level, the request body should look like this:
{
"term": {
"parent_uid": null,
"order": 2
}
}
When rearranging terms under an existing term on a different level, the request body should look like this:
{
"term": {
"parent_uid": "term_1",
"order": 5
}
}
When reordering terms under an existing term on the same level (reorder term), the request body should be structured as follows:
{
"term": {
"parent_uid": "term_3",
"order": 1
}
}
Delete a term
The Delete a term request deletes an existing term and all the child terms within it.
To confirm the deletion of a term, you need to specify the force=true query parameter.
Note: When you delete a term, its existing associations with entries are removed. Additionally, the child terms will also eliminate associations with existing entries.
Get all terms across all taxonomies
The Get all terms across all taxoomies request returns comprehensive information of all the terms across all taxonomy available in a particular stack in your organization.
Note: The parameter $all in the URL is a reserved keyword in this context. It is used to refer to all taxonomies.
Global Fields
A Global field is a reusable field (or group of fields) that you can define once and reuse in any content type within your stack. This eliminates the need (and thereby time and efforts) to create the same set of fields repeatedly in multiple content types.
You can now pass the branch header in the API request to fetch or manage modules located within specific branches of the stack. Additionally, you can also set the include_branch query parameter to true to include the _branch top-level key in the response. This key specifies the unique ID of the branch where the concerned Contentstack module resides.
Additional Resource: You can create a dynamic and flexible Global field either by nesting Global field within the Modular Block or Group field within Global field
Get All Global Fields
The Get all global fields call returns comprehensive information of all the global fields available in a particular stack in your account.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.global-fields.management:read scope.
Get Single Global Field
The Get a single global field request allows you to fetch comprehensive details of a specific global field.
When executing the API call, in the 'URL Parameters' section, provide the unique ID of your global field. To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.global-fields.management:read scope.
Create Global Field
The Create a global field request allows you to create a new global field in a particular stack of your Contentstack account. You can use this global field in any content type within your stack.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.global-fields.management:write scope.
Note: Only the stack owner, administrator, and developer can create global fields.
Update Global Field
The Update a global field request allows you to update the schema of an existing global field.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.global-fields.management:write scope.
When executing the API call, in the 'URL Parameters' section, provide the unique ID of your global field.
Delete Global Field
The Delete global field request allows you to delete a specific global field.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.global-fields.management:write scope.
Warning: If your Global field has been referred within a particular content type, then you will need to pass an additional query parameter force:true to delete the Global field.
When executing the API call, in the 'URL Parameters' section, provide the unique ID of your global field.
Import Global Field
The Import a global field call imports a global field into a stack.
To import, you need to provide/upload a JSON file that contains the schema of the global field that you wish to import.
Tip: You can try the call manually in any REST API client, such as Postman, by passing a 'Body' parameter named global_field and selecting the input type as 'File'. Then, select the JSON file of the global field that you wish to import.
Export Global Field
This request is used to export a specific global field and its schema. The data is exported in JSON format. The exported file won’t get downloaded automatically. To download the exported file, a REST API client, such as Postman can be used.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.global-fields.management:write scope.
Entries
An entry is the actual piece of content created using one of the defined content types.
You can now pass the branch header in the API request to fetch or manage modules located within specific branches of the stack. Additionally, you can also set the include_branch query parameter to true to include the _branch top-level key in the response. This key specifies the unique ID of the branch where the concerned Contentstack module resides.
Get all Entries
The Get all entries call fetches the list of all the entries of a particular content type. It also returns the content of each entry in JSON format. You can also specify the environment and locale of which you wish to get the entries.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.entries.management:read scope.
Additionally, if you wish to fetch the metadata attached to each entry, then you need to pass include_metadata as a query parameter. Set this parameter to true to include the entry metadata along with all entries in the response body.
You will find the entry metadata under the _metadata key in the response. It will be associated with a specific extension UID as follows:
"_metadata": {
"extensions": {
"{extension_uid}": [{
"image_copyrights": "Contentstack Branding",
"scope": "local"
}]
}
}
You can add queries to extend the functionality of this API call. Under the URL Parameters section, insert a parameter named query and provide a query in JSON format as the value.
Note: The taxonomy query operators cannot be used with GET requests in the Content Management API.
To learn more about the queries, refer to the Queries section of the Content Delivery API doc.
Additional Resource: If you want to retrieve all entries that are in a given workflow stage, you need to pass the query, _workflow.uid, where uid is the Workflow Stage UID.
Tip: This request returns only the first 100 entries of the specified content type. If you want to fetch entries other than the first 100 in your response, refer the Pagination section to retrieve all your entries in paginated form. Also, to include the publish details in the response, make use of the include_publish_details parameter and set its value to ‘true’. This query will return the publish details of the entry in every environment along with the version number that is published in each of the environment. In addition to entry publish details, the include_publish_details parameter also fetches the entry metadata publishing details in the response.
Get a Single Entry
The Get a single entry request fetches a particular entry of a content type.
The content of the entry is returned in JSON format. You can also specify the environment and locale of which you wish to retrieve the entries.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.entries.management:read scope.
Additionally, if you wish to fetch the metadata attached to each entry, then you need to pass include_metadata as a query parameter. Set this parameter to true to include the entry metadata along with all entries in the response body.
You will find the entry metadata under the _metadata key in the response. It will be associated with a specific extension UID as follows:
"_metadata": {
"extensions": {
"{extension_uid}": [{
"image_copyrights": "Contentstack Branding",
"scope": "local"
}]
}
}
Tip: To include the publish details in the response, make use of the include_publish_details parameter and set its value to ‘true’. This query will return the publish details of the entry in every environment along with the version number that is published in each of the environment. In addition to entry publish details, the include_publish_details parameter also fetches the entry metadata publishing details in the response.
Tip: Also, if no version is mentioned, this request will retrieve the latest published version of the entry. To retrieve a specific version, make use of the version parameter.
Create an EntryNEW
The Create an entry call creates a new entry for the selected content type.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.entries.management:write scope.
When executing the API call, in the 'Body' section, you need to provide the content of your entry based on the content type created.
Here are some important scenarios when creating an entry.
Scenario 1: If you have a reference field in your content type, here's the format you need to follow to add the data in the ‘Body’ section
{
"entry": {
"title": "Entry title",
"url": "Entry URL",
"reference_field_uid": [{
"uid": "blt111000d1e110b001",
"_content_type_uid": "referred_content_type_uid"
}]
}
}
Scenario 2: If you need to create an entry that contains asset files, you need to provide the asset UID(s) in the ‘Body’ section.
To add a single file, enter a single UID (file_field_uid). For multiple asset files, enter the asset files’ UIDs (file_field_uid_multiple) in an array. You need to use only one of the following formats.
Here's the JSON schema for both the cases:
{
"entry": {
"title": "Entry title",
"url": "Entry URL",
"file_field_uid": "asset_uid", // ‘File’ field marked ‘Single’
"file_field_uid_multiple": ["asset_uid1", "asset_uid2, ..."], // ‘File’ field marked ‘Multiple’
}
}
Scenario 3: If you need to add your asset file within a Rich Text Editor, use the following JSON schema:
{
"entry": {
"title": "Entry title",
"url": "Entry URL",
"rte_field_uid": "<p><img src=\"asset_URL\" data-sys-asset-uid=\"blt111000e1c110b011" alt=\"alternative_text\"></p>"
}
}
Note: In the above code, in place of rte-field-uid, you need to provide the UID of the Rich Text Editor field.
Create an Entry with JSON RTE
The Create an entry with JSON RTE request lets you create a new entry for a selected content type that contains a JSON RTE field.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.entries.management:write scope.
When executing the API call, in the 'Body' section, you need to provide the content of your entry based on the content type created.
If you selected the Embed Objects option while creating the content type, you can embed entries within your JSON RTE field. In the 'Body' section, you need to specify the details of the entry you wish to embed.
Note: When creating an entry with JSON RTE, if a duplicate doc_uid is detected, the request will throw a "Duplicate UID" error in the response.
The schema to embed an entry within the JSON RTE field is as follows:
{
"children":[
{
"text":"Embedded entry:",
"bold":true
},
{
"uid":"v4_unique_id",
"type":"reference",
"attrs":{
"class-name":"embedded-entry redactor-component inline-entry",
"content-type-uid":"content_type_uid",
"display-type":"inline_or_block",
"entry-uid":"uid_of_the_entry_you_want_to_embed",
"locale":"locale_code",
"type":"entry",
},
"children":[
{
"text":""
}
]
},
{
"text":"continued text after embedding an entry."
}
],
"type":"p",
"uid":"v4_unique_id",
"attrs":{
}
}
Note: The children block should be added while creating an entry with a referenced entry and asset to help point the cursor after embedding an entry or asset. The schema of this block is as follows:
{
"children":[
{
"text":""
}
]
}
The schema to embed assets within the JSON RTE field is as follows:
{
"children":[
{
"text":"Embedded asset:",
"bold":true
},
{
"uid":"v4_unique_id",
"type":"reference",
"attrs":{
"asset-link":"asset_link",
"asset-name":"asset_name",
"asset-type":"image/jpg",
"asset-uid":"uid_of_the_asset_you_want_to_embed",
"class-name":"embedded-asset",
"content-type-uid":"sys_assets", //System generated typename that points to all referenced assets
"display-type":"display",
"inline":false,
"type":"asset",
},
"children":[
{
"text":""
}
]
},
{
"text":"continued text after embedding an asset",
"bold":true
}
],
"type":"p",
"uid":"v4_unique_id",
"attrs":{
}
}
Note: The UID within the block schema can be generated using any online V4 Unique ID generators. This block UID should be unique across the stack.
Create an Entry with Master Locale
The Create an entry with master locale request lets you create an entry in the master language of your stack if it does not already exist or has been deleted. You can use the UID of a localized entry to convert it into a master language entry.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.entries.management:write scope.
If the master language is not accessible or does not exist, a custom user role can still create an entry in any of the other available locales. However, the entry in the master language remains non-existent.
In such a scenario, roles with access to the master locale can create an entry in the master language using the UID of the localized entry and the copy_to_master query parameter. The copy_to_master parameter allows you to copy content from the localized entry to the master language entry version of the stack.
When executing the API call, in the ‘Body’ section, you need to provide the content of your entry based on the content type created. You also need to specify the UID of the localized entry for which you want to create an entry in the master locale.
Here’s what your request body should look like:
{
"entry": {
"title": "Entry in the master language",
"url": "/entry-in-the-master-language",
"tags": [],
"uid": "localized_entry_uid"
}
}
Create an entry with custom asset field
The Create an entry with custom asset field request is used to create an entry with a custom field that accepts data of type asset.
Create an entry with taxonomy
The Create an entry with taxonomy request lets you create a new entry for a selected content type that contains a taxonomy field.
In the “Body” section, you need to provide the content of your entry based on the content type created and the details of the taxonomy for the specified content type as follows:
{
"taxonomies":[
{
"taxonomy_uid":"taxonomy_uid_1",
"term_uid":"term_uid_1"
},
{
"taxonomy_uid":"taxonomy_uid_1",
"term_uid":"term_uid_2"
},
{
"taxonomy_uid":"taxonomy_uid_2",
"term_uid":"term_uid_2"
},
{
"taxonomy_uid":"taxonomy_uid_2",
"term_uid":"term_uid_3"
}
]
}
Update an Entry
The Update an entry call lets you update the content of an existing entry.
Passing the locale parameter will cause the entry to be localized in the specified locale.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.entries.management:write scope.
Note: The Update an entry call does not allow you to update the workflow stage for an entry. To update the workflow stage for the entry, use the Set Entry Workflow Stage call.
The Update an entry with JSON RTE call lets you update the content of an existing entry.
Passing the locale parameter will cause the entry to be localized in the specified locale.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.entries.management:write scope.
Note: While updating an entry with the JSON RTE field, the same block UID generated while creating an entry must be used.
The schema to update an embedded entry within the JSON RTE field is as follows:
{
"children":[
{
"text":"Embedded entry:",
"bold":true
},
{
"uid":"v4_unique_id",
"type":"reference",
"attrs":{
"class-name":"embedded-entry redactor-component inline-entry",
"content-type-uid":"content_type_uid",
"display-type":"inline_or_block",
"entry-uid":"uid_of_the_entry_you_want_to_embed",
"locale":"locale_code",
"type":"entry",
},
"children":[
{
"text":""
}
]
},
{
"text":"continued text after embedding an entry updated."
}
],
"type":"p",
"uid":"v4_unique_id",
"attrs":{
}
}
The schema to update an embedded asset within the JSON RTE field is as follows:
{
"children":[
{
"text":"Embedded asset:",
"bold":true
},
{
"uid":"v4_unique_id",
"type":"reference",
"attrs":{
"asset-link":"asset_link",
"asset-name":"asset_name",
"asset-type":"image/jpg",
"asset-uid":"uid_of_the_asset_you_want_to_embed",
"class-name":"embedded-asset",
"content-type-uid":"sys_assets",
"display-type":"display",
"inline":true,
"type":"asset",
},
"children":[
{
"text":""
}
]
},
{
"text":"continued text after embedding an asset",
"bold":true
}
],
"type":"p",
"uid":"v4_unique_id",
"attrs":{
}
}
Atomic Updates to Entries
Atomic operations are particularly useful when we do not want content collaborators to overwrite data. Though it works efficiently for singular fields, these operations come handy especially in case of fields that are marked as “Multiple”.
To achieve data atomicity, we have provided support for following atomic operators: PUSH, PULL, UPDATE, ADD, and SUB.
PUSH Operation
The PUSH operation allows you to “push” (or append) data into an array without overriding an existing value.
For example, you have an entry with a Number field (named “Multiple Number”), marked as “Multiple” and with the data, “1,” “4,” “5,” and you need to add “2” and “3” to it. In this case, you need to use the PUSH operation as follows:
{
"entry": {
"multiple_number": {
"PUSH": {
"data": [
2,
3
]
}
}
}
}
Say you need to push specific data (say “abc”) into a field named “Demo Field” which is within a “Group” field marked as “Multiple”. You need to use the “PUSH” operator as follows:
{
"entry": {
"multiple_group": {
"PUSH": {
"data": {
"demo_field": "abc"
}
}
}
}
}
PULL Operation
ThePULL operationallows you to pull data from an array field based on a query passed.
For example, you have an entry with a “Number” field named “Multiple Number” which has the values, “1,” “2,” “3,” “4,” and “5”, and you need to remove “2” and “ 3”. You need to use the PULL operation as follows:
{
"entry": {
"multiple_number": {
"PULL": {
"query": {
"$in": [
2,
3
]
}
}
}
}
}
Another example is if you need to pull specific field data from a field (say a “Group” field) marked as “Multiple,” where the field name is “Demo Field” and the specific value to be pulled is “abc”. You need to use the “PULL” operator as follows:
{
"entry": {
"multiple_group": {
"PULL": {
"query": {
"demo_field": {
"$in": ["abc"]
}
}
}
}
}
}
Note: Here are certain limitations to the PULL request:
1. Currently, a PULL operation on multiple fields will retrieve the result of only ONE field i.e., if you include multiple fields in your PULL request, you will be able to retrieve the data of only the first mentioned field.
2. PULL query does not work on Nested Group fields.
UPDATE Operation
The UPDATE operation allows you to update data at a specific index. This operation works for both singular fields and fields marked “Multiple”.
For example, you have an entry with a “Number” (named “Multiple Number”) field which has the values, “6,” “2,” “3,” “4,” and “5”, and you need to replace the number at the first index (a[0]) i.e., “6” with “1”. In this case, you need to use the UPDATE operation as follows:
{
"entry": {
"multiple_number": {
"UPDATE": {
"index": 0,
"data": 1
}
}
}
}
UPDATE Operation for Group Field
For example, consider a multi-group field - "banner" with 2 instances, and with titles “banner 1” and “banner 2”. Using the update operation, to replace the title at the second instance (a[1]) i.e., “Banner 2” with “New update” and link title at the second index with "New level 2 update through CMA call". In this case, you need to use the UPDATE operation as follows:
{
"entry": {
"group": {
"UPDATE": {
"index": 1,
"data": {
"title": "New update",
"link": {
"UPDATE": {
"data": {
"title": "New level 2 update through CMA call"
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
Thus, using the UPDATE operation you can update a single/multi-level group field without sending the whole object array.
UPDATE Operation for Nested Modular Blocks
For example, consider the following modular blocks nesting scenario:
Within "content_container" modular blocks, there is a "link_module" block. Within the link_module block, there are "link_components" modular blocks. Within the link_components modular blocks, there is a "link_component" block. In such nested modular blocks scenario, single line fields can be updated with the following Update operation:
{
"entry": {
"title": "example",
"content_container": {
"UPDATE": {
"index": 1,
"data": {
"link_module": {
"module_title": "test link module 2 Updated testing 2 new",
"link_components": {
"UPDATE": {
"index": 1,
"data": {
"link_component": {
"teaser": "updated Nested Module teaser using CMA call"
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
Thus, using the UPDATE operation, you can update single/multi-level fields within the nested modular blocks without sending the whole object array.
Atomic Operators for Number Fields
Contentstack provides support for atomic operators that will specifically help you to work with “Number” fields. These atomic operators include ADD and SUB.
ADD Operation
The ADD operation reads the latest value of a “Number” field and increments it by a numeric passed along with the operator. The increment occurs irrespective of what the current value of the field is.
For example, you have a “Number” field and you want to increment the value of the field by one. In this case, you need to use the "ADD":1 operation. This operation reads the latest value of the field, increments it by 1, and replaces the existing value of the field with the new value.
SUB Operation
The SUB operation works the opposite of ADD. It reads the latest value of a “Number” field and decrements it by a numeric value passed along with the operator.
For example, you have a “Number” field and you want to decrease the value of the field by one. In this case, you need to use the "SUB":1 operation. This operation reads the latest value of the field, decrements it by 1, and replaces the existing value of the field with the new value.
Delete an Entry
The Delete an entry request allows you to delete a specific entry from a content type. This API request also allows you to delete single and/or multiple localized entries.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.entries.management:write scope.
This API Request supports the following actions as well:
- Delete specific localized entry: For this request, you need to only specify the locale code of the language in the locale query parameter. If the locale parameter is not been specified, by default, the master language entry will be deleted.
- Delete master language along with all its localized entries: For this request, instead of the locale query parameter, you need to pass the delete_all_localized:true query parameter.
Note: The delete_all_localized parameter will work only if you are deleting localized versions from the master language.
- Delete multiple localized entry: Additionally, you can delete specific localized entries by passing the locale codes in the Request body using the locales key as follows:
{ "entry": { "locales": ["hi-in", "mr-in", "es"] } }
Entry Version Naming
Version naming allows you to assign a name to a version of an entry for easy identification. For more information, refer to the Name Entry Version documentation.
The Set Version Name for Entry request allows you to assign a name to a specific version of an entry.
In the request body, you need to specify the version name to be assigned and the locale of the entry.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.entry:write scope.
Tip: You can add an additional parameter force:true to force update the version name of the master entry.
The Get Details of All Versions of an Entry request allows you to retrieve the details of all the versions of an entry.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.entry:read scope.
The version details returned include the actual version number of the entry; the version name along with details such as the assigned version name, the UID of the user who assigned the name, and the time when the version was assigned a name; and the locale of the entry.
Note: If an entry is unlocalized, the version details of entries published in the master locale will be returned.
The Delete Version Name of Entry request allows you to delete the name assigned to a specific version of an entry. This request resets the name of the entry version to the version number.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.entry:write scope.
Entry References
The Get references of an entry call returns all the entries of content types that are referenced by a particular entry.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.entry:read scope.
Entry Languages
The Get languages of an entry call returns the details of all the languages that an entry exists in.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.entry:read scope.
Localize an Entry
The Localize an entry request allows you to localize an entry i.e., the entry will cease to fetch data from its fallback language and possess independent content specific to the selected locale.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.entries.management:write scope.
In the "Body" parameter, you need to provide the content of your entry based on the content type.
Note: This request will only create the localized version of your entry and not publish it. To publish your localized entry, you need to use the Publish an entry request and pass the respective locale code in the locale={locale_code} parameter.
Additional Resource: Refer the Localization docs for more information.
Unlocalize Entry
The Unlocalize an entry request is used to unlocalize an existing entry. Read more about Unlocalization.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.entry:write scope.
Export Entry
The Export an entry call is used to export an entry. The exported entry data is saved in a downloadable JSON file.The exported file won’t get downloaded automatically. To download the exported file, a REST API client, such as Postman can be used.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.entries:export scope.
Import Entry
The Import Entry calls given below help you to import entries by uploading JSON files.
Tip: You can try the call manually in any REST API client, such as Postman. You can export the required entry's JSON file, make the necessary changes to the data and then import the entry. While importing, you need to pass a form-data parameter named entry and select the input type as 'File'. Then, select the JSON file of the entry that you wish to import.
The Import an entry call is used to import an entry. To import an entry, you need to upload a JSON file that has entry data in the format that fits the schema of the content type it is being imported to.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.entries:import scope.
The Import an existing entry call will import a new version of an existing entry. You can create multiple versions of an entry.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.entries:import scope.
Publish Entry
The Publish an entry request lets you publish an entry either immediately or schedule it for a later date/time.
Note: When you publish an entry, the associated metadata of that entry will also get published. However, when publishing entries in bulk, the associated metadata of the entries will not get published.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.entry:publishscope.
In the 'Body' section, you can specify the locales and environments to which you want to publish the entry. When you pass locales in the "Body", the following actions take place:
- If you have not localized your entry in any of your stack locales, the Master Locale entry gets localized in those locales and are published
- If you have localized any or all of your entries in these locales, the existing localized content of those locales will NOT be published. However, if you need to publish them all, you need to perform a Bulk Publish operation.
The locale and environment details should be specified in the ‘entry’ parameter. However, if you do not specify any source locale(s), it will be published in the master locale automatically.
Along with the above details, you also need to mention the master locale and the version number of your entry that you want to publish.
In case of Scheduled Publishing, add the scheduled_at key and provide the date/time in the ISO format as its value. Example: "scheduled_at":"2016-10-07T12:34:36.000Z"
The Publish an Entry With References request allows you to publish an entry along with all its references at the same time.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.bulk-operations:publish scope.
Note: At a time, you can publish an entry in up to 50 languages and on 10 environments.
In the “Body” section, you need to specify the following parameters:
- entries: Pass the details of the main entry i.e., its entry UID, content type UID, the locale code, and the version that you want to publish.
- locales: Pass the locale codes in which you want to publish your entry and its references. If you do not specify a source locale, the entries will be published in the master locale automatically.
- environments: Pass the UIDs of the environments to which you want to publish the entries. You can get the UIDs from Get all environments request.
Here are some additional parameters that you need to pass in the “Request Body”:
- "publish_with_reference": true: Pass this parameter to publish an entry along with its references.
Note: Only one level of referenced entries will be published using this API Request.
- skip_workflow_stage_check: true: Pass this parameter to skip those entries that do not satisfy the workflow stage of their publishing rule(s) and publish the rest of them.
Note: Specifically applicable for Workflow enabled organizations, when this parameter is set to “false” and if any one of the entries fails to satisfy the set conditions, NONE of the entries will be sent for publishing.
- approvals: true: Pass this parameter to publish only those entries that have been approved by the designated approver, and skip the rest that have not yet been approved.
Note: Specifically applicable for Workflow enabled organizations, when this parameter is set to “false” and if any one of the entries is not approved by the Approver, NONE of the entries will be sent for publishing.
Unpublish Entry
The Unpublish an entry call will unpublish an entry at once, and also, gives you the provision to unpublish an entry automatically at a later date/time.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.entry:unpublish scope.
In the 'Body' section, you can specify the locales and environments from which you want to unpublish the entry. These details should be specified in the ‘entry’ parameter. However, if you do not specify a locale, it will be unpublished from the master locale automatically.
You also need to mention the master locale and the version number of your entry that you want to publish.
In case of Scheduled Unpublishing, add the scheduled_at key and provide the date/time in the ISO format as its value. Example: "scheduled_at":"2016-10-07T12:34:36.000Z"
Assets
Assets refer to all the media files (images, videos, PDFs, audio files, and so on) uploaded in your Contentstack repository for future use.
You can now pass the branch header in the API request to fetch or manage modules located within specific branches of the stack. Additionally, you can also set the include_branch query parameter to true to include the _branch top-level key in the response. This key specifies the unique ID of the branch where the concerned Contentstack module resides.
These files can be attached and used in multiple entries.
Get All Assets
The Get all assets request returns comprehensive information on all assets available in a stack.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.assets.management:read scope.
Additionally, if you wish to fetch the metadata attached to each asset, then you need to pass include_metadata as a query parameter. Set this parameter to true to include the asset metadata along with all assets in the response body.
You will find the asset metadata under the _metadata key in the response. It will be associated with a specific extension UID as follows:
"_metadata":{
"extensions":{
"{extension_uid}":[
{
"image_copyrights": "Contentstack Branding",
"scope”: “local”
}
]
}
}
You can add queries to extend the functionality of this API call. Under the URL Parameters section, insert a parameter named query and provide a query in JSON format as the value.
To learn more about the queries, refer to the Queries section of the Content Delivery API doc.
Tip: To include the publish details in the response, make use of the include_publish_details parameter and set its value to ‘true’. This query will return the publish details of the entry in every environment along with the version number that is published in each of the environment. When you publish an asset, the associated metadata of that asset will also get published.
Get a Single Asset
The Get an asset request returns comprehensive information about a specific version of an asset of a stack.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.assets.management:read scope.
Additionally, if you wish to fetch the metadata attached to each asset, then you need to pass include_metadata as a query parameter. Set this parameter to true to include the asset metadata along with all assets in the response body.
You will find the asset metadata under the _metadata key in the response. It will be associated with a specific extension UID as follows:
"_metadata":{
"extensions":{
"{extension_uid}":[
{
"image_copyrights": "Contentstack Branding",
"scope”: “local”
}
]
}
}
Tip: To include the publish details in the response, make use of the include_publish_details parameter and set its value to ‘true’. This query will return the publish details of the entry in every environment along with the version number that is published in each of the environment. When you publish an asset, the associated metadata of that asset will also get published. However, when publishing assets in bulk, the associated metadata of the assets will not get published.
Get Assets of a Specific Folder
The Get assets of a specific folder retrieves all assets of a specific asset folder; however, it doesn't retrieve the details of subfolders within it.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.assets.management:read scope.
Get Assets and Subfolders of a Parent Folder
The Get assets and folders of a parent folder retrieves details of both assets and asset subfolders within a specific parent asset folder.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.assets.management:read scope.
Upload Asset
The Upload asset request uploads an asset file to your stack.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.assets.management:write scope.
To upload assets from your local system to Contentstack and manage their details, you need to use the following "form-data" parameters:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| asset[upload] (mandatory) | Select the input type as 'File'. Then, browse and select the asset file that you want to import. Most file types are supported. |
| asset[parent_uid] (optional) | If needed, assign a parent folder to your asset by passing the UID of the parent folder. |
| asset[title] (optional) | Enter a title for your uploaded asset. |
| asset[description] (optional) | Enter a description for your uploaded asset. |
| asset[tags] (optional) | Assign a specific tag(s) to your uploaded asset. |
You can try the call manually in any REST API client, such as Postman. Here's a screenshot for reference:
For easier access, here's the cURL for this API Request:
curl -X POST \
https://api.contentstack.io/v3/assets?include_dimension=true \
-H 'api_key: {api_key_of_your_stack}' \
-H 'authtoken: {your_authtoken}' \
-H 'cache-control: no-cache' \
-H 'content-type: multipart/form-data; boundary=----WebKitFormBoundary7MA4YWxkTrZu0gW' \
-F 'asset[upload]=@{Filepath e.g., /C:/Users/abc/Desktop/Sample.png}' \
-F 'asset[parent_uid]={If you need to add this file under an existing asset folder, pass the UID of the parent folder.}' \
-F 'asset[title]={If needed, enter a title for your uploaded asset.}' \
-F 'asset[description]={If needed, enter a description for your uploaded asset.}'
-F 'asset[tags]={If needed, assign a specific tag to your uploaded asset.}'
In the above cURL command, pass the necessary values within the curly brackets. The asset[parent_uid], asset[title], asset[description], asset[tags], and include_dimension=true parameters are optional. You can skip them if not required.
Replace Asset
The Replace asset call will replace an existing asset with another file on the stack.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.assets.management:write scope.
Tip: You can try the call manually in any REST API client, such as Postman.
Under 'Body', pass a body parameter named asset[upload] and select the input type as 'File'. This will enable you to select the file that you wish to import.
You can assign a parent folder to your asset by using the asset[parent_uid] parameter, where you can pass the UID of the parent folder.
Additionally, you can pass optional parameters such as asset[title] and asset[description] which let you enter a title and a description for the uploaded asset, respectively.
Generate Permanent Asset URLNEW
The Generate Permanent Asset URL request allows you to generate a permanent URL for an asset. This URL remains constant irrespective of any subsequent updates to the asset.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.assets.management:write scope.
Warning: You can generate the permanent asset URL and update the asset details only once. Once done, you can no longer make changes to the permanent URL.
In the request body, you need to pass the permanent URL in the following format:
{
"asset": {
"permanent_url": "https://images.contentstack.io/v3...{stack_api_key}/{asset_uid}/{unique_identifier}"
}
}
In the above URL, you can pass any unique identifier (slug) that suits your requirement.
Another way to generate a permanent URL for an asset is to pass the URL as a form-data parameter, i.e., asset[permanent_url]. In that case, the Content-Type in the Headers section must be changed from application/json to multipart/form-data. You can provide the permanent URL of your choice (along with a slug) as a value for this parameter, for example:
https://{base_URL}/v3/assets/{stack_api_key}/{asset_uid}/{slug}
Download an Asset with Permanent URLNEW
The Download an asset with permanent URL request displays an asset in the response. The asset returned in the response can be saved to your local storage system. Make sure to specify the unique identifier (slug) in the request URL.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.assets:download scope.
This request will return the most recent version of the asset, however, to download the latest published version of the asset, pass the environment query parameter with the environment name.
Note: Before executing this API request, ensure to create a permanent URL for the asset you want to download.
Delete Asset
The Delete asset call will delete an existing asset from the stack.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.assets.management:write scope.
Rich Text Editor Assets
The Get information on RTE assets call returns comprehensive information on all assets uploaded through the Rich Text Editor field.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.assets.rt:read scope.
Asset Version Naming
Version naming allows you to assign a name to a version of an asset for easy identification. For more information, refer the Name Asset Versions documentation.
The Set Version Name for Asset request allows you to assign a name to a specific version of an asset.
In the request body, you need to specify the version name to be assigned to the asset version.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.asset:writescope.
The Get Details of All Versions of an Asset request allows you to retrieve the details of all the versions of an asset.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.asset:read scope.
The details returned include the actual version number of the asset; the version name along with details such as the assigned version name, the UID of the user who assigned the name, and the time when the version was assigned a name; and the count of the versions.
The Delete Version Name of Asset request allows you to delete the name assigned to a specific version of an asset. This request resets the name of the asset version to the version number.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.asset:write scope.
Asset Reference
The Get asset references request returns the details of the entries and the content types in which the specified asset is referenced.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.asset:read scope.
Retrieve Specific Asset Types
The Get either only images or videos request retrieves assets that are either image or video files, based on query request.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.assets.management:read scope.
You can add queries to extend the functionality of this API call. Under the URL Parameters section, insert a parameter named query and provide a query in JSON format as the value.
To learn more about the queries, refer to the Queries section of the Content Delivery API doc.
Update Asset Details
The Update asset revision call upgrades a specified version of an asset as the latest version of that asset.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.assets.management:write scope.
Under 'Body', you need to specify the asset version number that you want to make the latest in raw JSON format, and also provide a "Title" and a "Description" for the asset. Another way to provide a "Title" and a "Description" for the asset is to pass them as optional form-data parameters, i.e., asset[title] and asset[description].
Here's an example of the raw body:
{
"asset": {
"title": "Title",
"description": "Description"
},
"version": 3
}
The Update asset request allows you to update the title and description of an asset.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.assets.management:write scope.
Note: Here are some points to keep in mind:
1. You can also use this request to generate a permanent URL for your asset, which remains constant irrespective of any further updates to the asset.
2. This call updates only the meta data of an asset. To replace an asset, try the Replace asset request under Asset Collection.
Under 'Body', you need to pass the updated details of "Title" and "Description" is in the form of 'raw' body as follows:
{
"asset":{
"title":"new title",
"description":"updated description"
}
}
Another way to provide a "Title" and a "Description" for the asset is to pass them as optional form-data parameters, i.e., asset[title] and asset[description]. You can assign a parent folder to your asset by using the asset[parent_uid] parameter, where you need to pass the UID of the parent folder.
Publish Asset
The Publish an asset call is used to publish a specific version of an asset on the desired environment either immediately or at a later date/time.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.asset:publish scope.
Note: When you publish an asset, the associated metadata of that asset will also get published. However, when publishing assets in bulk, the associated metadata of the assets will not get published.
In case of Scheduled Publishing, add the scheduled_at key and provide the date/time in the ISO format as its value. Example: "scheduled_at":"2016-10-07T12:34:36.000Z"
In the 'Body' section, enter the asset details, such as locales and environments, where the assets need to be published. These details should be in JSON format.
Unpublish Asset
The Unpublish an asset call is used to unpublish a specific version of an asset from a desired environment.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.asset:unpublish scope.
In case of Scheduled Unpublishing, add the scheduled_at key and provide the date/time in the ISO format as its value. Example: "scheduled_at":"2016-10-07T12:34:36.000Z"
In the 'Body' section, enter the asset details, such as locales and environments, from where the assets need to be unpublished. These details should be in JSON format.
Asset Folder Collection
The Get a single folder call gets the comprehensive details of a specific asset folder by means of folder UID.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.assets.management:read scope.
When executing the API call to search for a subfolder, you need to provide the parent folder UID.
The Get a single folder by name call retrieves a specific asset folder based on the name provided.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.assets.management:read scope.
The Get subfolders of a parent folder request retrieves the details of only the subfolders of a specific asset folder. This request does not retrieve asset files.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.assets.management:read scope.
The Create a folder call is used to create an asset folder and/or add a parent folder to it (if required). To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.assets.management:write scope.
In the ‘Body’ section, you need to provide a name for the new folder.
If you want to place this folder within another folder, provide the UID of the parent folder in the Request body as follows:
{
"asset": {
"name": "asset_folder_name",
"parent_uid": "asset_parent_folder_uid"
}
}
Note: Here are some points that needs to be considered when executing this API request:
- A maximum of 300 folders can be created.
- The maximum level of folder nesting is 5.
- When nesting folder, you cannot nest a folder within the same folder or within its child folders.
The Update or move folder request can be used either to update the details of a folder or set the parent folder if you want to move a folder under another folder.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.assets.management:write scope.
When executing the API request, provide the UID of the folder that you want to move/update.
In the ‘Body’ section, you need to provide a new name for your folder, and if you want to move your folder within another folder, then you need provide the UID of the parent folder.
Note: Here are some points that needs to be considered when executing this API request:
- A maximum of 300 folders can be created.
- The maximum level of folder nesting is 5.
- When nesting folder, you cannot nest a folder within the same folder or within its child folders.
The Delete a folder call is used to delete an asset folder along with all the assets within that folder.
When executing the API call, provide the parent folder UID.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.assets.management:write scope.
Embed Entries and Assets in the Rich Text Editor
You can embed other entries and/or assets inside the Rich Text Editor (RTE) field while creating entries. Inside the RTE field, you can embed entries inline; at the block level; or as a hyperlink; and assets as downloadable entities or simply display them (for images).
Note: This feature is available only if it is part of your plan. To avail of this feature, you can get in touch with our Support team.
The embedded items are added as HTML components within the RTE, and their contents change dynamically as and when you modify the source item. When retrieved or modified, these embedded HTML components are returned in the API response as JSON objects.
You can now pass the branch header in the API request to fetch or manage modules located within specific branches of the stack. Additionally, you can also set the include_branch query parameter to true to include the _branch top-level key in the response. This key specifies the unique ID of the branch where the concerned Contentstack module resides.
Additional Resource: Refer to the “Utils SDK” of our SDKs to understand how you can render embedded entries and assets using the Contentstack SDKs.
Create a content type with embedded RTE objects
The Create a content type with embedded RTE objects request lets you create a content type, which supports embedded objects inside its RTE field.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.content-types.management:write scope.
In the “Body” section, you need to provide the complete schema of the content type (refer JSON schema for creating a content type).
To embed entries within a specific RTE, pass the reference_to parameter with valid content type UIDs to determine entries of which content type(s) can be embedded inside the editor.
Note: The max number of content types that can be referenced within a single Rich Text Editor field is 10.
To embed assets within a specific RTE, you can pass "sys_assets" value within the reference_to array along with the content type UIDs.
Here’s a sample schema of a Rich Text Editor field that supports embedded entries and assets:
{
"data_type":"text",
"display_name":"Sample RTE",
"uid":"sample_rich_text_editor",
"field_metadata":{
"..."
},
"reference_to":[
"content_type_UID_1",
"content_type_UID_1",
"sys_assets"
],
"..."
}
Additional Resource: Refer to the Rich Text Field Schema guide to understand how you can format the content entered in the field.
Update content type with embedded RTE objects
The Update content type with embedded RTE objects request allows you to update the schema of an existing content type that contains embedded entries and/or assets within its Rich Text Editor field. To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.content-types.management:write scope.
Note: Whenever you update a content type, it will auto-increment the content type version.
When executing the API request, in the “URL Parameters” section, provide the unique ID of your content type.
In the “Body” section, you need to provide the updated schema of your content type. You can refer the JSON schema for creating a content type document to know how you can add/update fields in your content type through API.
You can make changes to the schema of the Rich Text Editor field while updating the content type schema. Here is a sample of an updated Rich Text Editor schema:
{
"data_type":"text",
"display_name":"Updated RTE",
"uid":"updated_rich_text_editor",
"field_metadata":{
"allow_rich_text":true,
"description":"",
"multiline":false,
"rich_text_type":"advanced"
},
"reference_to":[
"content_type_UID_1",
"content_type_UID_2",
"sys_assets"
],
"mandatory":false,
"unique":false,
"non_localizable":false
}
Create an entry with embedded entries in RTE
The Create an entry with embedded RTE entries request allows you to embed entries inside the Rich Text Editor field while creating a new entry for the selected content type.
Note: Within a single Rich Text Editor field, you can embed a maximum of 100 components, entries and assets combined.
When executing the API request, in the 'Body' section, you need to provide the content of your entry based on the fields present within the content type created.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.entries.management:write scope.
If your entry contains a Rich Text Editor field, you can embed entry/entries of the same or other content types inside the field as HTML components. These embedded entries can be added inline within the flow of content; as a separate content block; or as a dynamic hyperlink within the rich text.
Note: Only the Rich Text Editor fields of type Custom and Advanced support embedded objects. You cannot embed entries and/or assets inside a Basic editor.
Since we refer to an embedded entry as a separate HTML element, you need to wrap the entry component inside the <div> HTML tag. To refer to the entry of your choice and define what embedded style you prefer, specify the following attributes:
- class: To specify a class name for the HTML element (embedded entry)
- data-sys-entry-uid: To specify the unique ID of the entry that you want to embed inside the editor
- data-sys-entry-locale: To specify the locale code for the language in which the selected entry is localized
- data-sys-content-type-uid: To specify the unique ID of the content type to which the embedded entry belongs
- sys-style-type: You can pass inline, block, or link to specify how you want to embed the entry within the text
- type: To specify the type of object embedded inside the rich text, e.g., entry
Here’s a sample of rich text that contains embedded entries:
"rich_text_editor": "<p>Embedded entry as block:</p><div class=\"embedded-entry\" data-sys-entry-uid=\"bltb6ea3a0ab9699748\" data-sys-entry-locale=\"en-us\" data-sys-content-type-uid=\"sample_content_type\" sys-style-type=\"block\" type=\"entry\"></div><p>Embedded entry inline with text:</p><div class=\"embedded-entry\" data-sys-entry-uid=\"bltc2bcca1a99a89261\" data-sys-entry-locale=\"en-us\" data-sys-content-type-uid=\"sample_content_type\" sys-style-type=\"inline\" type=\"entry\"></div><p>Embedded entry as link:</p><a class='embedded-entry' data-sys-entry-uid='blt36e18c7c05db737b' data-sys-entry-locale='en-us' data-sys-content-type-uid='sample_content_type' sys-style-type='link' type='entry'></a>"
The above Rich Text Editor contains entries embedded as a separate content block; within the flow of text; and as a hyperlink to another Contentstack entry.
Note: Contentstack’s SDKs help consume the response returned when you create an entry containing embedded objects. You can then decide what content (fields of the embedded entry, for instance) should be rendered on the frontend.
Create an entry with embedded assets in RTE
The Create an entry with embedded RTE assets request allows you to embed assets inside the Rich Text Editor field while creating a new entry for the selected content type.
Note: Within a single Rich Text Editor field, you can embed a maximum of 100 components, entries and assets combined.
When executing the API request, in the 'Body' section, you need to provide the content of your entry based on the content type created.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.entries.management:write scope.
If your entry contains a Rich Text Editor field, you can embed assets inside the Rich Text as downloadable or display images within the rich text.
Note: Only the Rich Text Editor fields of type Custom and Advanced support embedded objects. You cannot embed entries and/or assets inside a Basic editor.
Since we refer to an embedded asset as a separate HTML element, you need to wrap the asset component inside the <div> HTML tag. To refer to the asset of your choice and define what embedded style you prefer, specify the following attributes:
- class: To specify a class name for the HTML element (embedded asset)
- data-sys-asset-uid: To specify the unique ID of the asset that you want to embed inside the editor
- sys-style-type: You can pass display or download to specify whether the embedded asset should be downloadable or act as a display image
- type: To specify the type of object embedded inside the rich text, e.g., asset
Tip: An embedded asset works exactly like the Reference field. When you update the details of an embedded asset or replace the source asset with another asset, the Rich Text Editor automatically updates the embedded HTML component with the latest version of that asset.
Here’s a sample of rich text that contains embedded assets:
"rich_text_editor": "<p>Embedded asset as display image:</p><img class=\"embedded-asset\" data-sys-asset-uid=\"blt8d49bb742bcf2c83\" type=\"asset\" sys-style-type=\"display\"></img><p>Embedded asset as downloadable image:</p><img class=\"embedded-asset\" data-sys-asset-uid=\"bltb47f1aa5ae422cd1\" type=\"asset\" sys-style-type=\"download\"></img>"
Note: Contentstack’s SDKs help consume the response returned when you create an entry containing embedded objects. You can then render the embedded assets on the frontend whenever required.
Update embedded RTE objects
The Update embedded RTE objects request lets you update the embedded entries or assets placed inside the Rich Text Editor field of an entry.
In the 'Body' section, provide the updated Rich Text Editor information in JSON format.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.entries.management:write scope.
Tip: You can either replace the embedded asset with another or change the style (downloadable or displayable) in which the asset has been embedded inside the editor.
Here’s a sample of updated Rich Text Editor content:
"rich_text_editor": "<p>Updated embedded asset to downloadable image:</p><img class=\"embedded-asset\" data-sys-asset-uid=\"blt120a5a04d91c9466\" type=\"asset\" sys-style-type=\"download\"></img><p>Updated embedded entry inline with text:</p><div class=\"embedded-entry\" data-sys-entry-uid=\"bltb6ea3a0ab9699748\" data-sys-entry-locale=\"en-us\" data-sys-content-type-uid=\"sample_content_type\" sys-style-type=\"inline\" type=\"entry\"></div>"
Get information on embedded RTE objects
The Get information on embedded RTE objects request returns comprehensive information on all entries and/or assets embedded within the Rich Text Editor field.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.entries.management:read scope.
If your entry contains a Rich Text Editor field and you wish to fetch the content schema of the items embedded inside the rich text, then you need to pass the include_embedded_items[]=BASE query parameter.
You can view information about the embedded objects under the _embedded_items parameter in the JSON response body.
Note: Contentstack’s Content Delivery SDKs help consume the embedded entries and assets returned in the API response. You can then render the embedded objects on the frontend however required.
Bulk Operations
You can perform bulk operations such as Publish, Unpublish, and Delete on multiple entries or assets, or Change the Workflow Details of multiple entries or assets at the same time.
Additional Resource: You can also learn how to perform bulk operations on search results.
Points to keep in mind:
- Each bulk publish API request publishes a maximum of 10 items per request, if the Bulk Publish feature is part of your plan. So, for example, if you publish 100 items, you need to make 10 Bulk API requests.
- Bulk actions do not follow the standard CMA rate limit of 10 requests per second. The default rate limit for bulk actions is 1 request per second i.e., in one second you can make only one bulk publish API request.
- Mentioning the version number of the entries is optional. If you don't specify the version number, the latest version of the entries will be published or unpublished.
- Bulk publishing of entries of all locals is not supported. However, you can specify the locales as an array (en-us, fr-fr, zh-zh, and so on) against the ‘locale’ parameter to get them published.
You can now pass the branch header in the API request to fetch or manage modules located within specific branches of the stack. This key specifies the unique ID of the branch where the concerned Contentstack module resides.
Bulk Publish Operation
The Publish entries and assets in bulk request allows you to publish multiple entries and assets at the same time.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.bulk-operations:publish scope.
Note: At a time, you can publish 10 entries in 10 languages and in 10 environments.
Additionally, nested references can be published up to five levels deep with all parent entries at the same time by passing api_version as 3.2 in the Headers section.
In the 'Body' section, you need to specify the locales (mention the locale codes) and environments (mention the names) to which you want to publish the entries or assets. If you do not specify a source locale, the entries or assets will be published in the master locale automatically.
Tip: To schedule the publishing of multiple entries and/or assets, you can make use of the ‘Create a Release’ request. Then, you can deploy this Release and all of the pinned items can be published together either immediately or at a scheduled time to whatever environment you choose.
Within the ‘entries’ parameter, pass these details of each entry – content type UIDs, entry UIDs, locales in which the entries are present, and the version (you need to specify the entry versions when schedule publishing) that you want to publish. Within the ‘assets’ parameter, pass these details of each entry – asset UIDs and the version that you want to publish (optional).
If some of the entries added to the bulk publish request do not satisfy the applied publish rules, then all the items will not be published. To publish at least the items that satisfy the publish rules, pass additional query parameters, skip_workflow_stage_check=true and approvals=true.
Let's understand how these two query parameters work while publishing entries.
When you use skip_workflow_stage_check=true as a query parameter, the entries that satisfy the publish rules are sent for publishing, while those entries that have not yet reached the workflow stage defined for the set publish rules will not be sent for publishing. However, if you set this parameter to false and some of the entries included in the bulk publish request have not yet reached the workflow stage defined for the set publish rules, then all the entries selected will not be sent for publishing.
When you use approvals=true as a query parameter, the entries that satisfy the publish rules are sent for publishing, while those entries that have not yet received authorization from the approver assigned to them will not be sent for publishing. However, if you set this parameter to false and some of the entries included in the bulk publish request have not yet received authorization from the approver assigned to them, then all the entries selected will not be sent for publishing.
Bulk Unpublish Operation
The Unpublish entries and assets in bulk request allows you to unpublish multiple entries and assets at the same time.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.bulk-operations:unpublish scope.
Note: At a time, you can unpublish 10 entries in 10 languages and on 10 environments. Additionally, you can pass api_version as 3.2 in the Headers section to get logs of your unpublish task as per the new nested flow.
In the 'Body' section, you need to specify the locales (mention the locale codes) and environments (mention the names) to which you want to unpublish the entries or assets. If you do not specify a source locale, the entries or assets will be unpublished in the master locale automatically.
Tip: To schedule the unpublishing of multiple entries and/or assets, you can make use of the ‘Create a Release’ request. Then, you can deploy this Release and all of the pinned items can be unpublished together either immediately or at a scheduled time to whatever environment you choose.
Within the ‘entries’ parameter, pass these details of each entry – content type UIDs, entry UIDs, locales in which the entries are present, and the version that you want to unpublish. Within the ‘assets’ parameter, pass these details of each entry – asset UIDs and the version that you want to unpublish (optional).
If some of the entries added to the bulk unpublish request do not satisfy the applied publish rules, then all the items will not be unpublished. To unpublish at least the items that satisfy the publish rules, pass additional query parameters, skip_workflow_stage_check=true and approvals=true.
Let's understand how these two query parameters work while unpublishing entries.
When you use skip_workflow_stage_check=true as a query parameter, the entries that satisfy the publish rules are sent for unpublishing, while those entries that have not yet reached the workflow stage defined for the set publish rules will not be sent for unpublishing. However, if you set this parameter to false and some of the entries included in the bulk unpublish request have not yet reached the workflow stage defined for the set publish rules, then all the entries selected will not be sent for unpublishing.
When you use approvals=true as a query parameter, the entries that satisfy the publish rules are sent for unpublishing, while those entries that have not yet received authorization from the approver assigned to them will not be sent for unpublishing. However, if you set this parameter to false and some of the entries included in the bulk unpublish request have not yet received authorization from the approver assigned to them, then all the entries selected will not be sent for unpublishing.
Bulk Delete Operation
The Delete entries and assets in bulk request allows you to delete multiple entries and assets at the same time.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.bulk-operations:delete scope.
Note: At a time, you can delete 10 entries in a bulk delete request.
In the 'Body' section, you need to specify the content type UIDs, entry UIDs or asset UIDs, and locales of which the entries or assets you want to delete.
Bulk Update Workflow Details Operation
The ‘Change Workflow Details’ action is a new option that allows you to change workflow details (such as stage, assignee, due date, and comments) of multiple entries at the same time.
Additional Resource: To know how you can change Workflow details of multiple entries at once, refer to the Change Workflow Details of Entries in Bulk article.
The Update workflow details in bulk request allows you to update the workflow details for multiple entries at the same time.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.bulk-operations:workflow scope.
Note: You can change the workflow stage of multiple entries only if all the entries have been assigned the same workflow stage and are associated with the same workflow.
In the 'Body' section, you need to provide the details of the workflow stage. Enter a comment for the assigned user, if needed; provide the due date; set notification settings to ‘true’, so that the specified user will be notified of it; enter the UID of the workflow stage; and finally, enter the user details, such as UID, name, and email address of the user.
Note: At a time, you can update the workflow details for 10 entries in a bulk update workflow details request. During the bulk update, if any one entry's workflow stage fails to update, then the workflow stage of all entries in the bulk operation will fail to update.
Within the ‘entries’ parameter, pass these details of each entry – content type UIDs, entry UIDs, and locales in which the entries are present.
Extensions
Extensions let you create custom fields and custom widgets that lets you customize Contentstack's default UI and behavior. Read more about Extensions.
You can now pass the branch header in the API request to fetch or manage modules located within specific branches of the stack. Additionally, you can also set the include_branch query parameter to true to include the _branch top-level key in the response. This key specifies the unique ID of the branch where the concerned Contentstack module resides.
Custom Fields
This type of extension lets you create custom fields that you can use in your content types. Read more About Custom Fields.
The Get all custom fields request is used to get the information of all custom fields created in a stack.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.extensions.management:read scope.
The Get a single custom field request gets the comprehensive details of a specific custom field.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.extensions.management:read scope.
The Upload a custom field request is used to upload a custom field to Contentstack.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.extensions.management:write scope.
In the ‘Body’ section, you need to provide the following ‘Body’ parameters under ‘form-data’:
- extension[upload]: Select the HTML file of the custom field that you want to upload
- extension[title]: Enter the title of the custom field that you want to upload
- extension[data_type]: Enter the data type for the input field of the custom field
- extension[tags]: Enter the tags that you want to assign to the custom field
- extension[multiple]: Enter ‘true’ if you want your custom field to store multiple values
- extension[type]: Enter type as ‘field’, since this is a custom field extension.
Tip: You can try the call manually in any REST API client, such as Postman. Under 'Body', for the extension[upload] parameter, select the input type as 'File'. This will enable you to select the file that you wish to import.
The Create a custom field with source URL call is used to create a custom field that is hosted externally.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.extensions.management:write scope.
In the ‘Body’ section, you need to provide details of the custom field, such as its tags, data type, title, external source link, set if the field is to take multiple values or not, and configuration details.
Note: The custom field has various data types you can select from – Text, Number, Date, Boolean, JSON, Reference, File, and Asset.
The Create a custom field with source code request is used to create a custom field in Contentstack by providing the source code of the extensions. This source code will be hosted on Contentstack.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.extensions.management:write scope.
In the ‘Body’ section, you need to provide details of the custom field, such as its tags, data type, title, source code of the extension, set if the field is to take multiple values or not, and configuration details.
Note: The custom field has various data types you can select from – Text, Number, Date, Boolean, JSON, Reference, File, and Asset.
The Update a custom field request is used to update the details of a custom field.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.extensions.management:write scope.
In the ‘Body’ section, you need to provide details of the custom field, such as its tags, data type, title, external source link (or the updated external source code), set if the field is to take multiple values or not, and configuration details.
The Delete custom field request is used to delete a specific custom field.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.extensions.management:write scope.
The Create Content Type with Extension Field request is used to create a content type that includes a custom field.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.content-types.management:write scope.
Custom Widgets
This type of extensions lets you add widgets that help you analyze content of an entry and recommend content ideas. Read more About Custom Widgets.
The Get widgets request is used to get the information of all custom widgets created in a stack.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.extensions.management:read scope.
The Get widgets of a content type request gets the comprehensive details of all widgets that are assigned to a specific content type.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.extensions.management:read scope.
The Upload a widget request is used to upload a new custom widget to a stack.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.extensions.management:write scope.
In the ‘Body’ section, you need to provide the following ‘Body’ parameters under ‘form-data’:
- extension[upload]: Select the HTML file of the widget that you want to upload
- extension[title]: Enter the title of the widget that you want to upload
- extension[tags]: Enter the tags that you want to assign to the widget
- extension[scope]: Enter either {"content_types":["$all"]} or {"content_types":["content_type_uid1”, “content_type_uid2”, “..."]} to apply this widget to all content types or specific content types, respectively
- extension[type]: Enter type as ‘widget’, since this is a custom widget extension
Tip: You can try the call manually in any REST API client, such as Postman. Under 'Body', for the extension[upload] parameter, select the input type as 'File'. This will enable you to select the file that you wish to import.
The Create Widget with source URL call is used to create a widget that is hosted externally.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.extensions.management:write scope.
In the ‘Body’ section, you need to provide details of the widget, such as its tags, title, external source link (src), configuration details, set if the extension is a widget or field, and specify the scope, i.e., the content types to which you want to apply the widget.
The Create widget with source code request is used to create a widget in Contentstack by providing the source code. This source code will be hosted on Contentstack.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.extensions.management:write scope.
In the ‘Body’ section, you need to provide details of the widget, such as its tags, title, source code of the widget, configuration details, set if the extension is a widget or field, and specify the scope i.e., the content types that you want to apply the widget.
The Update a widget request is used to update the details of a widget.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.extensions.management:write scope.
In the ‘Body’ section, you need to provide details of the widget, such as its tags, title, external source link (or the updated external source code), configuration details, set if the extension is a widget or field, and specify the scope i.e., the content types that you want to apply the widget.
The Delete a widget call is used to delete a specific custom widget.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.extensions.management:write scope.
Dashboard Widgets
This type of extension lets you create widgets for your dashboard. Read more About Custom Dashboard Widgets.
The Get All Dashboard Widgets request is used to get the information of all the enabled custom dashboard extension.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.extensions.management:read scope.
The Upload Dashboard Widget request uploads the widget to the Stack Dashboard.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.extensions.management:write scope.
In the ‘Body’ section, you need to provide the following ‘Body’ parameters under ‘form-data’:
- extension[upload]: Select the HTML file of the widget that you want to upload.
- extension[title]: Enter the title of the widget that you want to upload.
- extension[tags]: Enter the tags that you want to assign to the widget.
- extension[type]: Enter type as ‘dashboard’, since this is a custom widget extension.
The Create a Dashboard Widget with Source URL request is used to upload an extension hosted externally.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.extensions.management:write scope.
In the ‘Body’ section, you need to provide details of the dashboard widget, such as its tags, title, external source link (src), configuration details, and set if the extension is a widget or field.
The Create dashboard widget with source code request is used to create a widget in Contentstack by providing the source code. This source code will be hosted on Contentstack.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.extensions.management:write scope.
In the ‘Body’ section, you need to provide details of the widget, such as its tags, title, source code of the widget, configuration details, and set if the extension is a widget or field.
The Update dashboard widget request is used to update the details of an widget.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.extensions.management:write scope.
In the ‘Body’ section, you need to provide details of the extension, such as its tags, data type, title, and configuration details.
The Delete a dashboard widget call is used to delete a specific custom dashboard.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.extensions.management:write scope.
JSON RTE PluginsNEW
This type of extension lets you add customized plugins to your JSON Rich Text Editor and extend its functionality. Read more About JSON RTE Plugins.
The Get all JSON RTE plugins request is used to get the information of all JSON Rich Text Editor plugins created in a stack.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.extensions.management:read scope.
The Get a single JSON RTE plugin request gets the comprehensive details of a specific JSON Rich Text Editor plugin.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.extensions.management:read scope.
The Create a JSON RTE plugin with source URL request allows you to add an externally hosted JSON RTE plugin to your stack.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.extensions.management:writescope.
In the ‘Body’ section, you need to provide details of the JSON RTE plugin, such as its tags, title, external source link, set if the field is to take multiple values or not, configuration details, and the extension type. Enter the extension type as ‘rte_plugin’, since this is a JSON RTE plugin extension.
Note: You can add a maximum of 50 extensions (including custom fields , custom widgets and JSON RTE plugins) in a stack.
The Update a JSON RTE plugin request allows you to update the details of an existing JSON RTE plugin.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.extensions.management:write scope.
In the ‘Body’ section, you need to provide details of the JSON RTE plugin, such as its tags, title, external source link (or the updated external source code), set if the field is to take multiple values or not, configuration details, and the extension type.
The Delete JSON RTE plugin request allows you to delete a specific JSON RTE plugin.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.extensions.management:write scope.
The Create content type with JSON RTE plugin request allows you to create a content type that includes JSON RTE plugins within the JSON Rich Text Editor.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.content-types.management:write scope.
In the “Body” section, you need to provide the UIDs of the JSON RTE plugins you want to add within the plugins parameter.
The schema for this is as follows:
"plugins":[
"bag98lo5467qs532l0c",
"ang22qw1234pl345g8j",
"pnr65op1258hs807k9l"
]
Note: The maximum number of JSON RTE plugins that can be added to a single JSON RTE field in a content type is five.
Asset Sidebar ExtensionsNEW
This type of extension lets you add widgets with more capabilities or custom functionalities for editors to manage, transform, and optimize stack assets. Read more about Asset Sidebar Extensions.
The Get all asset sidebar extensions request is used to get the information of all the asset sidebar extensions created in a stack.
The Get a single asset sidebar extension request gets the comprehensive details of a specific asset sidebar extension.
The Create an asset sidebar extension with source URL request allows you to add an externally hosted asset sidebar extension to your stack.
In the ‘Body’ section, you need to provide details of the asset sidebar extension, such as the extension type, title, configuration details, external source link, width, and blur effect. Enter the extension type as asset_sidebar_widget, since this is an asset sidebar extension.
The popup panel width should be within the range of 335 to 1024 pixels. Set the blur effect to true if you want to blur the details of the uploaded file by default.
Note: You can add a maximum of 50 extensions (including custom fields , custom widgets, JSON RTE plugins, and asset sidebar extensions) in a stack.
The Update an asset sidebar extension request allows you to update the details of an existing asset sidebar extension.
In the ‘Body’ section, you need to provide details of the asset sidebar extension, such as the extension type, title, configuration details, external source link (or the updated external source code), width, and blur effect.
The popup panel width should be within the range of 335 to 1024 pixels. Set the blur effect to true if you want to blur the details of the uploaded file by default.
The Delete asset sidebar extension request allows you to delete a specific asset sidebar extension.
Metadata for Entries and AssetsNEW
Metadata is a piece of information that lets you describe or classify an asset/entry.
You can manage your digital entities effectively and facilitate enhanced accessibility with additional metadata.
Note: The Metadata feature allows users to update their asset metadata or entry metadata without incrementing the asset or entry version.
Note: An extension or app is required to use Metadata APIs.
Get Metadata
The Get metadata request fetches the metadata attached to a specific asset or entry of a stack.
In the URL, you need to pass the unique ID of the metadata against the metadata_uid parameter.
Keep the following points in mind when getting metadata:
- To retrieve metadata for a specific entry or asset, you need to have read access to that entry or asset.
- You must pass the include_publish_details query parameter to fetch the metadata publishing details in the response.
Get All Metadata
The Get All Metadata request returns comprehensive information of all the metadata attached to all the entries and assets in your stack.
Note: Limited keys such as entity_uid, content_type_uid etc. are shown to the user with no access. For eg: You will see limited keys in the third object of the example response body as the user has no access to that particular entry in the stack.
Create Metadata
The Create metadata request lets you create metadata for a specific asset or entry. Whenever you create metadata for an entry or asset, you need to specify the extension to which it will be connected.
In the ‘Body’ section, you need to provide the following information:
- entity_uid: Specify the unique ID of the entry or asset for which you want to create metadata.
- type: Specify whether you want to create metadata for an entry or asset.
Note: The default type is an asset if not mentioned.
- _content_type_uid: Specify the content type UID if you are creating metadata for an entry.
Note: For an asset type, the content type UID will be "sys_assets".
- extension_uid: Specify the UID of the extension for which you want to create the metadata.
- locale: Specify the language in which the entry is localized if the type is an entry.
- metadata key: Specify the additional metadata that you want to attach to an existing asset/entry under a key name that suits your need.
Note: The metadata size allowed per extension per entry/asset is 5KB. Please get in touch with our support team for any queries.
Note: You can provide any key name to store the metadata for your entry or asset except the following prebuilt keys: created_by, updated_by, created_at, updated_at, deleted_at, api_key, scope, locale, type, extension_uid, _version.
Update Metadata
The Update metadata request lets you update the metadata for a specific entry or asset.
In the ‘Body’ section, you need to provide the metadata key, that specifies the additional metadata that you want to attach to an existing asset/entry under a key name that suits your need.
Note: The metadata size allowed per extension per entry/asset is 5KB. Please get in touch with our support team for any queries.
You can partially update metadata for a defined key without having to specify all the key details every time you update metadata.
Keep the following points in mind when updating metadata:
- To create/update metadata for a specific entry or asset, you need update access to that entry or asset.
- If you update entry or asset metadata once, then you cannot recover the previous version of the metadata.
Note: You can provide any key name to store the metadata for your entry or asset except the following prebuilt keys: created_by, updated_by, created_at, updated_at, deleted_at, api_key, scope, locale, type, extension_uid, _version, publish_details.
Delete Metadata
The Delete metadata request lets you delete the metadata associated with a specific entry or asset.
In the URL, you need to pass the unique ID of the metadata that you want to delete against the metadata_uid parameter.
Keep the following points in mind when deleting metadata:
- To delete metadata for a specific entry or asset, you need delete access to that entry or asset.
- Once you delete entry or asset metadata, it is permanently deleted and cannot be restored.
Publish Metadata
The Publish metadata request lets you publish the metadata associated with a specific entry or asset.
In the URL, you need to pass the unique ID of the metadata that you want to publish against the metadata_uid parameter.
Keep the following points in mind when publishing metadata:
- When you publish an entry/asset, the associated metadata of that entry/asset will also get published. However, when publishing entries/assets in bulk, the associated metadata of the assets/entries will not get published.
- You must pass the include_publish_details query parameter to fetch the metadata publishing details in the response.
Unpublish Metadata
The Unpublish metadata request lets you unpublish the metadata associated with a specific entry or asset.
In the URL, you need to pass the unique ID of the metadata that you want to unpublish against the metadata_uid parameter.
Labels
Labels allow you to group a collection of content within a stack. Using labels you can group content types that need to work together. Read more about Labels.
You can now pass the branch header in the API request to fetch or manage modules located within specific branches of the stack. Additionally, you can also set the include_branch query parameter to true to include the _branch top-level key in the response. This key specifies the unique ID of the branch where the concerned Contentstack module resides.
Labels Collection
Get all labels call fetches all the existing labels of the stack.
When executing the API call, under the 'Header' section, you need to enter the API key of your stack and the authtoken that you receive after logging into your account.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.labels.management:read scope.
You can add queries to extend the functionality of this API call. Under the URL Parameters section, insert a parameter named query and provide a query in JSON format as the value.
To learn more about the queries, refer to the Queries section of the Content Delivery API doc.
The Get label call returns information about a particular label of a stack.
When executing the API call, under the 'Header' section, you need to enter the authtoken that you receive after logging into your account.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.labels.management:read scope.
Add label call is used to create a label.
When executing the API call, under the 'Header' section, you need to enter the API key of your stack and the authtoken that you receive after logging into your account.
In the 'Body' section, enter the label details, such as the name of the label, the uid of the parent label, and the content types that need to be included in the label. These details need to be provided in JSON format.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.labels.management:write scope.
The Update label call is used to update an existing label.
When executing the API call, under the 'Header' section, you need to enter the authtoken that you receive after logging into your account.
In the 'Body' section, enter the updated details of your label, which include the name of the label, the uid of the parent label, and the content types that need to be included in the label. These details need to be provided in JSON format.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.labels.management:write scope.
The Delete label call is used to delete a specific label.
When executing the API call, under the 'Header' section, you need to enter the authtoken that you receive after logging into your account.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.labels.management:write scope.
Releases
You can pin a set of entries and assets (along with the deploy action, i.e., publish/unpublish) to a ‘release’, and then deploy this release to an environment. This will publish/unpublish all the items of the release to the specified environment. Read more about Releases.
You can now pass the branch header in the API request to fetch or manage modules located within specific branches of the stack. Additionally, you can also set the include_branch query parameter to true to include the _branch top-level key in the response. This key specifies the unique ID of the branch where the concerned Contentstack module resides.
Releases Collection
The Get all Releases request retrieves a list of all Releases of a stack along with details of each Release.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.releases.management:read scope.
The Get a single Release request gets the details of a specific Release in a stack.
When executing the API request, provide the Release UID as parameter.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.releases.management:read scope.
The Create a Release request allows you to create a new Release in your stack. To create a release, you need to provide the name of the release in the request body.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.releases.management:write scope.
The Update a Release call allows you to update the details of a Release, i.e., the ‘name’ and ‘description’.
When executing this API request, provide the Release UID as parameter. In the 'Body' section, you need to provide the new name and description of the Release that you want to update.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.releases.management:write scope.
The Delete a Release request allows you to delete a specific Release from a stack.
When executing the API request, provide the Release UID.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.releases.management:write scope.
Release ItemsNEW
The Get all items in a Release request retrieves a list of all items (entries and assets) that are part of a specific Release.
When executing the API request, you need to provide the Release UID.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.release:read scope.
The Add a single item to a Release request allows you to add an item (entry or asset) to a Release.
When executing the API request, you need to provide the Release UID. In the 'Body' section, you need to provide the details of the item such as the UID, version (of the entry and asset), content type UID (of an entry), the action to be performed (publish/unpublish), and the locale of the item. To add the asset in the release, the content type should be passed as "content_type_uid": "built_io_upload" in the request body.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.release:write scope.
The Add multiple items to a Release request allows you to add multiple items (entries and/or assets) to a Release.
When executing the API request, you need to provide the Release UID. In the 'Body' section, you need to provide the details of the items such as their UIDs, versions (in case of entries and assets), content type UIDs (in case of entries), the action to be performed (publish/unpublish), and the locales of the items. To add the asset in the release, the content type should be passed as "content_type_uid": "built_io_upload" in the request body.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.release:write scope.
Note: In a single request, you can add maximum 25 items (entries/assets) to a Release.
The Update Release items to their latest versions request let you update all the release items (entries and assets) to their latest versions before deployment.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.release:write scope.
In the 'Body' section, you need to specify the following:
{
"items":[
"$all"
]
}
Note: This API request only allows you to collectively update all items in the release to their latest versions and not update any particular item individually.
In case an un-localized entry in the release has been localized later, this request will update the entry to the latest localized version. For example, if you add an un-localized entry to a release and later localize it to the French (France) language, this API request will update the release with the localized French version of the entry.
Note: You cannot update the release items under the following scenarios:
If the updated version of an entry has new references, this API request doesn't automatically add the references to the release. You need to add them manually.
You cannot update the items in a release once you deploy it.
If the latest version of an entry is in the in-progress state, this API request doesn't update the entry.
The Remove an item from a Release request removes one or more items (entries and/or assets) from a specific Release.
When executing the API request, provide the Release UID. In the 'Body' section, you need to provide the details of the item such as their UIDs, version (of the entry), content type UID (of an entry), the action to be performed (publish/unpublish), and the locale of the item.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.release:write scope.
The Delete multiple items from a Release request deletes one or more items (entries and/or assets) from a specific Release.
When executing the API request, provide the Release UID. In the 'Body' section, you need to provide the UIDs of the items along with details such as their locale, versions, the action to be performed on the items (publish/unpublish), and content type UID of entries (if any).
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.release:write scope.
Deploy/Execute a Release
The Deploy a Release request deploys a specific Release to specific environment(s) and locale(s).
When executing the API request, provide the Release UID. In the 'Body' section, you need to provide the details of the Release that you want to deploy. For example, you need to provide the scheduled time (in case of scheduled release), action, and environment(s) on which the Release should be deployed.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.release:deploy scope.
Clone a Release
The Clone a Release request allows you to clone (make a copy of) a specific Release in a stack.
When executing the API request, provide the Release UID. In the 'Body' section, you need to provide the new name and description of the cloned Release.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.release:clone scope.
Workflows
Workflow is a tool that allows you to streamline the process of content creation and publishing, and lets you manage the content lifecycle of your project smoothly. For more information, refer to our Workflows documentation.
Get All Workflows
The Get all Workflows request retrieves the details of all the Workflows of a stack.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.workflows.management:read scope.
Get a Single Workflow
The Get a Single Workflow request retrieves the comprehensive details of a specific Workflow of a stack.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.workflows.management:read scope.
Create a Workflow
The Create a Workflow request allows you to create a Workflow.
In the 'Body' section, you can provide the details of the workflow that includes name, content types, owners, description, and workflow stages of your Workflow. To define the branch scope, specify the unique IDs of the branches for which the workflow will be applicable in the following schema in the request body:
"branches":[
"main",
"development"
]
To control who can edit an entry at different stages of the workflow, you can pass the entry_lock parameter inside each workflow stage.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.workflows.management:write scope.
Note: Workflow superusers, organization owners, and stack owners/admins can edit or delete the entry in any workflow stage, irrespective of the stage access rules set for that stage.
You can assign any one of the following values to this parameter:
- $none: This is the default value for all workflow stages. This value allows all users to have edit access over the entry at any workflow stage until the value for the entry_lock parameter is changed.
- $others: Set the entry_lock parameter to $others to allow only those users who have stage transition rights to edit the entry in the current workflow stage.
- $all: Set the entry_lock parameter to $all to restrict all users from accessing the entry.
Note: Users with stage transition rights, however, will still be able to change the workflow stage of the entry.
Note: The entry is available for editing, by default, in the first stage that you create in your workflow. As a result, the entry_lock parameter is set to $none for the first stage in the workflow.
Add or Update Workflow Details
The Add or Update Workflow request allows you to add a workflow stage or update the details of the existing stages of a workflow.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.workflows.management:write scope.
In the 'Body' section, you can provide the updated details of the name, content types, owners, description, and workflow stages of your Workflow. To define the branch scope, specify the unique IDs of the branches for which the workflow will be applicable in the following schema in the request body:
"branches":[
"main",
"development"
]
To control who can edit an entry at different stages of the workflow, you can pass the entry_lock parameter inside each workflow stage.
Note: Workflow superusers, organization owners, and stack owners/admins can edit or delete the entry in any workflow stage, irrespective of the stage access rules set for that stage.
You can assign any one of the following values to this parameter:
- $none: This is the default value for all workflow stages. This value allows all users to have edit access over the entry at any workflow stage until the value for the entry_lock parameter is changed.
- $others: Set the entry_lock parameter to $others to allow only those users who have stage transition rights to edit the entry in the current workflow stage.
- $all: Set the entry_lock parameter to $all to restrict all users from accessing the entry.
Note: Users with stage transition rights, however, will still be able to change the workflow stage of the entry.
Note: The entry is available for editing, by default, in the first stage that you create in your workflow. As a result, the entry_lock parameter is set to $none for the first stage in the workflow.
Disable Workflow
The Disable Workflow request allows you to disable a workflow.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.workflows.management:write scope.
Enable Workflow
The Enable Workflow request allows you to enable a workflow.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.workflows.management:write scope.
Delete Workflow
The Delete Workflow request allows you to delete a workflow.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.workflows.management:write scope.
Entry Workflow Stages
The Set Entry Workflow Stage request allows you to either set a particular workflow stage of an entry or update the workflow stage details of an entry.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.entry.workflow:write scope.
In the 'Body' section, you need to provide the details of the workflow stage. Enter a comment for the assigned user, if needed; provide the due date; set notification settings to ‘true’, so that the specified user will be notified of it; enter the UID of the workflow stage; and finally, enter the user details, such as UID, name, and email address of the user.
Note: The request operates using a management token only when the transition rule is configured to "All users/roles."
Publish Rules Collection
The Create Publish Rules request allows you to create publish rules for the workflow of a stack.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.workflows.publishing-rules:write scope.
To define the branch scope, specify the unique IDs of the branches for which the publishing rule will be applicable in the following schema in the request body:
"branches":[
"main",
"development"
]
The Update Publish Rules request allows you to add a publish rule or update the details of the existing publish rules of a workflow.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.workflows.publishing-rules:write scope.
To define the branch scope, specify the unique IDs of the branches for which the publishing rule will be applicable in the following schema in the request body:
"branches":[
"main",
"development"
]
The Delete Publish Rules request allows you to delete an existing publish rule.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.workflows.publishing-rules:write scope.
The Get all Publish Rules request retrieves the details of all the Publish rules of a workflow.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.workflows.publishing-rules:read scope.
The Get a Single Publish Rule request retrieves the comprehensive details of a specific publish rule of a Workflow.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.workflows.publishing-rules:read scope.
Publish Rules by Content Types
The Get Publish Rules by Content Types request allows you to retrieve details of a Publish Rule applied to a specific content type of your stack.
When executing the API request, in the 'Header' section, you need to provide the API Key of your stack and the authtoken that you receive after logging into your account.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.workflows.management:read scope.
Publish Request Approval
This multipurpose request allows you to either send a publish request or accept/reject a received publish request.
When executing the API request, in the 'Header' section, you need to provide the API Key of your stack and the authtoken that you receive after logging into your account.
In the 'Body' section, you need to provide the details of the publish rule, such as its UID, action (‘publish’, ‘unpublish’, or ’both’), status (this could be ‘0’ for Approval Requested, ‘1’ for ‘Approval Accepted’, and ‘-1’ for ‘Approval Rejected’), notification setting, and comment for the approver.
Workflow Tasks
The Get all Tasks request retrieves a list of all tasks assigned to you.
When executing the API request, in the 'Header' section, you need to provide the API Key of your stack and the authtoken that you receive after logging into your account.
Languages
Contentstack has a sophisticated multilingual capability. It allows you to create and publish entries in any language. This feature allows you to set up multilingual websites and cater to a wide variety of audience by serving content in their local language(s).
Read more about Languages.
You can now pass the branch header in the API request to fetch or manage modules located within specific branches of the stack. Additionally, you can also set the include_branch query parameter to true to include the _branch top-level key in the response. This key specifies the unique ID of the branch where the concerned Contentstack module resides.
Language Collection (Locales)
This call fetches the list of all languages (along with the language codes) available for a stack.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.languages.management:read scope.
When executing the API call, under the 'Header' section, you need to enter the authtoken that you receive after logging into your account.
You can add queries to extend the functionality of this API call. Under the URL Parameters section, insert a parameter named query and provide a query in JSON format as the value.
To learn more about the queries, refer to the Queries section of the Content Delivery API doc.
This call lets you add a new language to your stack. You can either add a supported language or a custom language of your choice.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.languages.management:write scope.
When executing the API call, under the 'Header' section, you need to enter the API key of your stack and the authtoken that you receive after logging into your account.
In the 'Body' section, enter the language name and code in JSON format. You can also specify the fallback language you want to assign to the new language within the same JSON.
Warning: Once generated, you cannot modify a custom language code. However, you can update the language name and fallback language if required.
The Get a language call returns information about a specific language available on the stack.
When executing the API call, under the 'Header' section, you need to enter the authtoken that you receive after logging into your account.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.languages.management:read scope.
The Update language call will let you update the details (such as display name) and the fallback language of an existing language of your stack.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.languages.management:write scope.
When executing the API call, under the 'Header' section, you need to enter the authtoken that you receive after logging into your account.
In the 'Body' section, enter the updated details of your language name and fallback language in JSON format.
The Delete language call deletes an existing language from your stack.
When executing the API call, under the 'Header' section, you need to enter the API key of your stack and the authtoken that you receive after logging into your account.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.languages.management:write scope.
Fallback Languages
Language fallback allows entries created in a particular language to initially inherit data from the fallback language instead of directly inheriting content from the master language. For more information, refer the documentation for Fallback Language.
The Set a fallback language request allows you to assign a fallback language for an entry in a particular language.
When executing the API call, under the 'Header' section, you need to enter the API key of your stack and the authtoken that you receive after logging in to your account.
In the 'Body' section, enter the language codes in JSON format.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.languages.management:write scope.
Note: The language set as a fallback language will always inherit data from the master language if it does not have localized content.
The Update fallback language request allows you to update the fallback language for an existing language of your stack.
When executing the API call, under the 'Header' section, you need to enter the API key of your stack and the authtoken that you receive after logging in to your account.
In the 'Body' section, enter the updated details of the fallback language in JSON format.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.languages.management:write scope.
Note: The language set as a fallback language will always inherit data from the master language if it does not have localized content.
Environment
A publishing environment corresponds to one or more deployment servers or a content delivery destination where the entries need to be published.
Read more about Environments.
Environment Collection
The Get all environments call fetches the list of all environments available in a stack.
You can add queries to extend the functionality of this API call. Under the URL Parameters section, insert a parameter named query and provide a query in JSON format as the value.
To learn more about the queries, refer to the Queries section of the Content Delivery API doc.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include thecm.environments.management:read scope.
The Get a single environment call returns more details about the specified environment of a stack.
When executing the API call, under the 'Header' section, you need to enter the authtoken that you receive after logging into your account.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.environments.management:read scope.
The Add an environment call will add a publishing environment for a stack.
When executing the API call, under the 'Header' section, you need to enter the API key of your stack and the authtoken that you receive after logging into your account.
In the 'Body' section, mention the environment name, the URLs (which include the language code and the URL of the server).
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.environments.management:write scope.
The Update environment call will update the details of an existing publishing environment for a stack.
When executing the API call, under the 'Header' section, you need to enter the API key of your stack and the authtoken that you receive after logging into your account.
In the 'Body' section, enter the updated details of the environment. You can modify the environment name, the URLs (which include the language code and the URL of the server).
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.environments.management:write scope.
The Delete environment call will delete an existing publishing environment from your stack.
When executing the API call, under the 'Header' section, you need to enter the API key of your stack and the authtoken that you receive after logging into your account.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.environments.management:write scope.
Tokens
Contentstack provides different types of tokens to authorize API requests. You can use Delivery Tokens to authenticate Content Delivery API (CDA) requests and retrieve the published content of an environment. To authenticate Content Management API (CMA) requests over your stack content, you can use Management Tokens.
Delivery tokens provide read-only access to the associated environments, while management tokens provide read-write access to the content of your stack. Use these tokens along with the stack API key to make authorized API requests.
Delivery Token Collection
The Get all delivery tokens request returns the details of all the delivery tokens created in a stack.
The Get a single delivery token request returns the details of a particular delivery token created in a stack.
The Create delivery token request is used to create a delivery token in the stack.
In the Request Body, you need to pass the details of the delivery token in JSON format. The details include the name, description, and the environment of the delivery token.
To create a delivery token with associated preview token, pass the create_with_preview_token query parameter as true.
Note: It is highly recommended to set only one publishing environment per delivery token.
You need to specify the branch and alias scope for your delivery token through the following schema in the request body:
{
"module":"branch",
"branches":[
"main",
"development"
],
"acl":{
"read":true
}
},
{
"module":"branch_alias",
"branch_aliases":[
"deploy",
"release"
],
"acl":{
"read":true
}
}
The Update delivery token request lets you update the details of a delivery token.
In the Request Body, you need to pass the updated details of the delivery token in JSON format. The details include the updated name, description, and/or the environment of the delivery token.
You need to specify the branch and alias scope for your delivery token through the following schema in the request body:
{
"module":"branch",
"branches":[
"main",
"development"
],
"acl":{
"read":true
}
},
{
"module":"branch_alias",
"branch_aliases":[
"deploy",
"release"
],
"acl":{
"read":true
}
}
The Delete delivery token request deletes a specific delivery token.
Preview Token CollectionNEW
A Preview Token provides you access to retrieve details of your website within the live preview panel.
Note: The Preview tokens are exclusively compatible with the new rest-preview.contentstack.com endpoint.
The Create preview token request creates a Preview token for a particular Delivery token in a stack of your organization.
The Delete preview token request deletes a preview token associated with a specific delivery token.
Management Token Collection
The Get all management tokens request returns the details of all the management tokens generated in a stack and not the actual management tokens.
The Get a single management token request returns the details of a specific management token generated in a stack and not the actual management token.
The Create management token request is used to create a management token in a stack. This token provides you with read-write access to the content of your stack.
Note: A management token can only be generated by the owner or admin of a stack.
In the Request Body, you need to pass the details of the management token in JSON format. The details include the name, description, the stack-level permissions you need to assign to the token, and the expiry date of the token in UTC time (if required). Additionally, you can also choose to get notified (via email) seven days before the token expires.
You need to specify the branch and alias scope for your management token through the following schema in the request body:
{
"module":"branch",
"branches":[
"main",
"development"
],
"acl":{
"read":true
}
},
{
"module":"branch_alias",
"branch_aliases":[
"deploy",
"release"
],
"acl":{
"read":true
}
}
Note: You can generate a maximum of 10 management tokens for a specific stack within your organization.
The Update management token request lets you update the details of a management token. You can change the name and description of the token; update the stack-level permissions assigned to the token; and change the expiry date of the token (if set).
In the Request Body, you need to pass the updated details of the management token in JSON format.
To specify the updated branch and alias scope for your management token, use the following schema in the request body:
{
"module":"branch",
"branches":[
"main",
"development"
],
"acl":{
"read":true
}
},
{
"module":"branch_alias",
"branch_aliases":[
"deploy",
"release"
],
"acl":{
"read":true
}
}
The Delete management token request deletes a specific management token.
Roles
A role is a collection of permissions that will be applicable to all the users who are assigned this role.
Read more about Roles.
Role Collection
The Get all roles request returns comprehensive information about all roles created in a stack.
You can add queries to extend the functionality of this API request. Under the URL Parameters section, insert a parameter named query and provide a query in JSON format as the value.
To learn more about the queries, refer to the Queries section of the Content Delivery API doc.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.roles.management:read scope.
The Get a single role request returns comprehensive information on a specific role.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.roles.management:read scope.
The Create a role request creates a new role in a stack.
In the 'Body' section, mention the role name, description, users, additional roles, rules (includes the actions that can be performed on entries, fields, and/or assets), and permissions (which include the details of the content types, environments, and languages that are accessible).
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.roles.management:write scope.
Note: You can also restrict access to the master language entry while defining permissions for a new role. Refer to our Manage Language Permissions documentation for more details.
To add customized exceptions for all or specific languages, add an additional locale module in the request body. Under this module, pass the following parameters:
- locales: Specify the unique IDs of the languages for which you want to add exception rules
- sub_acl: Add this under acl. Here, specify the permissions you want to restrict for the languages specified in the above parameter, e.g., "create":true
- restrict: true: Set this parameter to true to enable exception rules for the specified languages
Here’s what your request body should look like:
{
"module":"locale",
"locales":[
"blt008a444c98ab47e8"
],
"acl":{
"read":true,
"sub_acl":{
"read":false,
"create":false,
"update":true,
"delete":false
}
},
"restrict":true
}
Note: Language-related exceptions can be added only for custom roles and the developer and content manager system roles.
When creating a user role, you need to specify the branch and alias scope through the following schema in the request body:
{
"module":"branch",
"branches":[
"main"
],
"acl":{
"read":true
}
},
{
"module":"branch_alias",
"branch_aliases":[
"deploy"
],
"acl":{
"read":true
}
}
The Update role request lets you modify an existing role of your stack. However, the pre-existing system roles cannot be modified.
In the 'Body' section, include the updated details of the role which include name, description, users, additional roles, rules (includes the actions that can be performed on entries, fields, and/or assets), and permissions (which include the details of the content types, environments, and languages that are accessible).
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.roles.management:write scope.
Note: You can also restrict access to the master language entry while defining permissions for a new role.
To add customized exceptions for all or specific languages, add an additional locale module in the request body. Under this module, pass the following parameters:
- locales: Specify the unique IDs of the languages for which you want to add exception rules
- sub_acl: Add this under acl. Here, specify the permissions you want to restrict for the languages specified in the above parameter, e.g., "create":true
- restrict: true: Set this parameter to true to enable exception rules for the specified languages
Here’s what your request body should look like:
{
"module":"locale",
"locales":[
"blt008a444c98ab47e8"
],
"acl":{
"read":true,
"sub_acl":{
"read":false,
"create":false,
"update":true,
"delete":false
}
},
"restrict":true
}
Note: Language-related exceptions can be added only for custom roles and the developer and content manager system roles.
When updating a user role, you need to specify the branch and alias scope through the following schema in the request body:
{
"module":"branch",
"branches":[
"main"
],
"acl":{
"read":true
}
},
{
"module":"branch_alias",
"branch_aliases":[
"deploy"
],
"acl":{
"read":true
}
}
The Delete role call deletes an existing role from your stack.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.roles.management:write scope.
Webhooks
A webhook is a mechanism that sends real-time information to any third-party app or service to keep your application in sync with your Contentstack account. Webhooks allow you to specify a URL to which you would like Contentstack to post data when an event happens. Read more about Webhooks.
Note: If any key name in the response data sent to a notification URL begins with a dollar sign ($), it will be prefixed with the acronym "cs" as a wildcard. For example, the key named "$success" would be replaced with "cs$success." For more information, refer to our API Change Log documentation.
Get all Webhooks
The Get all Webhooks request returns comprehensive information on all the available webhooks in the specified stack.
Tip: Execute this call when you wish to retrieve the UID of a webhook.
When executing the API call, under the 'Header' section, you need to enter the authtoken that you receive after logging into your account.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.webhooks.management:read scope.
Get Single Webhook
The Get webhook request returns comprehensive information on a specific webhook.
When executing the API call, under the 'Header' section, you need to enter the authtoken that you receive after logging into your account.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.webhooks.management:read scope.
Create a Webhook
The Create a webhook request allows you to create a new webhook in a specific stack.
In the “Body” section, you need to enter the name of the webhook; the destination details i.e., target urls, basic authentication details, and custom headers; and the channels; and set the disabled and concise_payload parameters as per requirement.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.webhooks.management:write scope.
Note: You can also set trigger conditions based on actions performed on entry comments and discussions. Refer to our Comments and Discussions webhook documentation to learn more about the trackable events.
The disabled parameter allows you to enable or disable the webhook. You can set its value to either false to enable the webhook and true to disable the webhook.
The concise_payload parameter allows you to send a concise JSON payload to the target URL when a specific event occurs. To send a comprehensive JSON payload, you can set its value to false. However, to send a concise payload, set the value of the concise_payload parameter to true.
When creating a webhook, you need to specify the branch scope through the following schema in the request body:
"branches":[
"main"
]
Update Webhook
The Update webhook request allows you to update the details of an existing webhook in the stack.
In the “Body” section, you need to enter new details such as the name of the webhook; the destination details i.e., target urls, basic authentication details, and custom headers; and the channels; or reset the disabled or concise_payload parameters as per requirement.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.webhooks.management:write scope.
The disabled parameter allows you to enable or disable the webhook. You can set its value to either false to enable the webhook and true to disable the webhook.
The concise_payload parameter allows you to send a concise JSON payload to the target URL when a specific event occurs. To send a comprehensive JSON payload, you can set its value to false. However, to send a concise payload, set the value of the concise_payload parameter to true.
When updating a webhook, you need to specify the branch scope through the following schema in the request body:
"branches":[
"main"
]
Delete Webhook
The Delete webhook call deletes an existing webhook from a stack.
When executing the API call, under the 'Header' section, you need to enter the API key of your stack and the authtoken that you receive after logging into your account.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.webhooks.management:write scope.
Export Webhook
The Export a Webhook request exports an existing webhook. The exported webhook data is saved in a downloadable JSON file. The exported file won’t get downloaded automatically. To download the exported file, a REST API client, such as Postman can be used.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.webhooks:export scope.
Import Webhook
The 'Import Webhook' section consists of the following two requests that will help you to import new Webhooks or update existing ones by uploading JSON files.
Note: You can try the call manually in any REST API client, such as Postman, by passing a 'Body' parameter named webhook under form-data. Select the input type as 'File' and select the JSON file of the webhook that you want to import.
The Import Webhook request imports a webhook. To import a webhook, you need to upload a JSON file with the webhook data.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.webhooks:import scope.
The Import an Existing Webhook request will allow you to update the details of an existing webhook.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.webhooks:import scope.
Get Webhook Executions
The Get executions of a webhook request allows you to fetch the execution details of a specific webhook, which includes the execution UID. These details are instrumental in retrieving webhook logs and retrying a failed webhook.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.webhook:read scope.
Note: You can retrieve webhook log information only for 30 days prior to the current day.
Each execution of a webhook is assigned a unique ID that allows you to gather information, such as request-response body, retry attempts, and so on, pertaining to a specific execution of the webhook.
To filter the webhook execution details based on a specific date range, you must pass from and to as query parameters. For both of these parameters, provide a date in ISO format as the value. For instance, to set the start date in the from parameter to December 8, 2017, you can pass the date in ISO format as shown below:
from="2017-12-08T00:00:00.000Z"
To filter the webhook execution details based on whether the webhook successfully ran or failed to execute, pass the query parameter under the URL Parameters section, and provide a query in JSON format as its value. Within the query, you can use the status key to filter the response as per your desired execution status.
The following table shows values you can use for the query parameter:
| Webhook Execution Status | Query JSON Value |
| Success | {
"status": {
"$gte": "200",
"$lte": "399"
}
}
|
| Failure | {
"status": {
"$gte": “400",
"$lte": “599"
}
}
|
This API request will return a maximum of 100 records while fetching the execution details for a specific webhook. Previously, there was no limit on the number of records returned. You can use the "skip" parameter to fetch older records. To limit the number of records returned, you can use the “limit” parameter.
Webhook Retry
This call makes a manual attempt to execute a webhook after the webhook has finished executing its automatic attempts.
When executing the API call, in the 'URL Parameter' section, enter the execution UID that you receive when you execute the 'Get executions of webhooks' call.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.webhooks.management:write scope.
Get Execution Log
Get latest execution log of a webhook call will return a comprehensive detail of all the webhooks that were executed at a particular execution cycle.
When executing the API call, in the 'URL Parameter' section, enter the execution UID that you receive when you execute the call.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.webhook:read scope.
Audit Log
Audit log displays a record of all the activities performed in a stack and helps you keep a track of all published items, updates, deletes, and current status of the existing content.
Read more about Audit Log.
You can now pass the branch header in the API request to fetch or manage modules located within specific branches of the stack. Additionally, you can also set the include_branch query parameter to true to include the _branch top-level key in the response. This key specifies the unique ID of the branch where the concerned Contentstack module resides.
Get Audit Log
The Get audit log request is used to retrieve the audit log of a stack.
You can apply queries to filter the results. Refer to the Queries section for more details.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.audit-logs:read scope.
Note: You can retrieve audit log information only for 30 days prior to the current day (for an organization).
Get Audit Log Item
The Get audit log item request is used to retrieve a specific item from the audit log of a stack.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.audit-logs:read scope.
Note: You can retrieve audit log information only for 30 days prior to the current day (for an organization).
Publish Queue
The Publish Queue displays the historical and current details of activities such as publish, unpublish, or delete that can be performed on entries and/or assets. It also shows details of Release deployments. These details include time, entry, content type, version, language, user, environment, and status.
For more details, refer the Publish Queue documentation.
You can now pass the branch header in the API request to fetch or manage modules located within specific branches of the stack. Additionally, you can also set the include_branch query parameter to true to include the _branch top-level key in the response. This key specifies the unique ID of the branch where the concerned Contentstack module resides.
Get Publish Queue
The Get publish queue request returns comprehensive information on activities such as publish, unpublish, and delete that have performed on entries and/or assets. This request also includes the details of the release deployments in the response body.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.publish-queue.management:read scope.
Note: You can retrieve the publish queue details for activities performed on entries and/or assets of your stack in the last 30 days. To retrieve publish queue details for nested reference published tasks, pass api_version parameter as 3.2 in the Headers section.
You can apply various queries such as count, limit, bulkJobId, include_job_details: true/false, etc. to filter the results. Refer to the Queries section for more details.
Now, you can limit the number of bulk job details in the response body to 25 items. Also, you can view the summary of your bulk jobs within the summary key in the response body.
Get Publish Queue Activity
The Get publish queue activity request returns comprehensive information on a specific publish, unpublish, or delete action that was performed on an entry and/or asset. You can also retrieve details of a specific release deployment.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.publish-queue.management:read scope.
Note: You can retrieve the publish queue details for activities performed in the last 30 days only.
You can apply queries to filter the results. Refer to the Queries section for more details.
Cancel Scheduled Action
The Cancel Scheduled Action request will allow you to cancel any scheduled publishing or unpublishing activity of entries and/or assets and also cancel the deployment of releases.
To configure the permissions for your application via OAuth, please include the cm.publish-queue.management:write scope.
Note: You must pass api_version:3.2 parameter in the Header section of the request to enable Nested References Publishing.
Postman Collection
About Contentstack Postman Collection
The Contentstack Postman collection is a set of preconfigured REST API requests that will make it easy for you to get started with the Contentstack APIs and try out our API requests through the popular Postman REST client.
Install Postman
To use the Contentstack Postman collection you will need to have the Postman. You can either download the Desktop app or use Postman for Web.
Note: If you have already installed Postman for your device, go to the Download Latest Postman Collection for Contentstack section.
Postman is available for Windows (x32), Windows (x64), Mac (Intel Chip / Apple Chip), and Linux environments.
Download Latest Collection
Once you have installed Postman on your device, click the Run in Postman button to start working with the Content Management API endpoints for Contentstack.
Note: The Contentstack Postman collection does not support the now deprecated Postman Chrome extension. Make sure you have installed the latest version of the Postman desktop app.
This opens the Fork collection into your workspace modal from where you can proceed to download/work with the Contentstack Postman collection in the following three ways:
- View the Collection
- Import a Copy of the Collection
- Fork the Collection
Let’s look at each of the above methods in detail.
View the Collection
This option allows you to just view (and not try out) the API requests of the Postman collection.
Perform the following steps to view the Content Management API Postman collection:
- Click the View collection link in the Fork collection into your workspace modal.
A new tab opens up in your browser where you should see the latest collection preloaded in the left navigation.
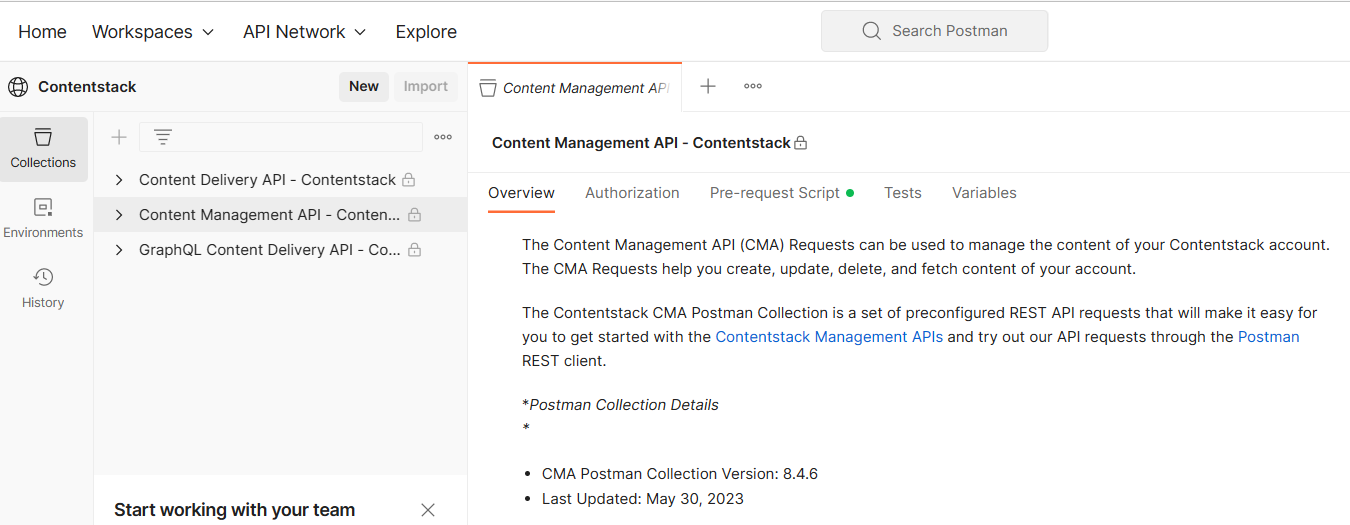
Note: If you want to try out the API requests, you can either import a copy of the collection or fork the collection.
Import a Copy of the Collection
This option allows you to import a copy of the collection into your workspace.
To import the Content Management API collection, perform the following steps:
- Click the import a copy link in the Fork collection into your workspace modal.
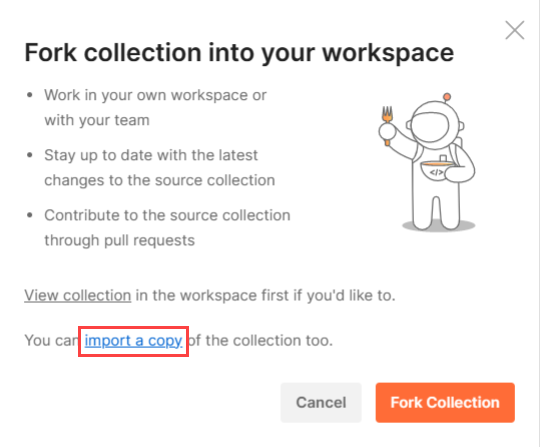
- In the resulting Import Collection modal within the Postman app, select a workspace and click Import to import the latest Postman collection into your selected workspace.
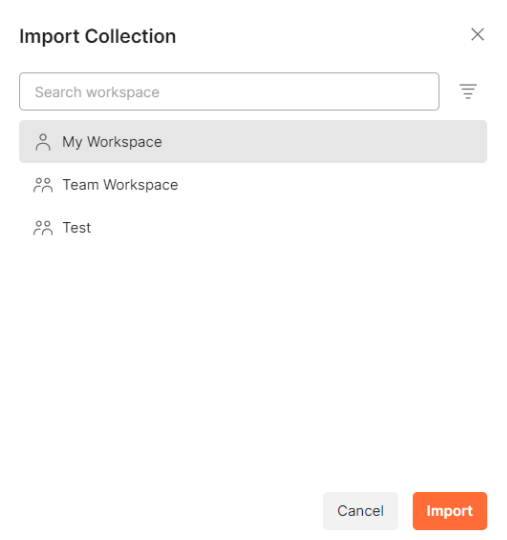
You will see a copy of the latest Postman collection in the left navigation panel.
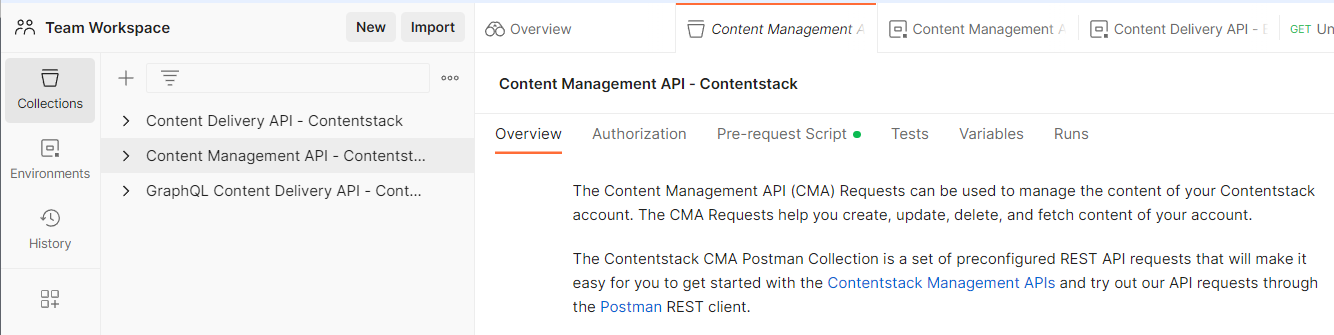
Fork the Collection
This option allows you to fork, or create a copy of the collection, and perform changes to the collection without affecting the original.
To fork the Content Management API collection, perform the following steps:
- Click the Fork Collection button in the Fork collection into your workspace modal.
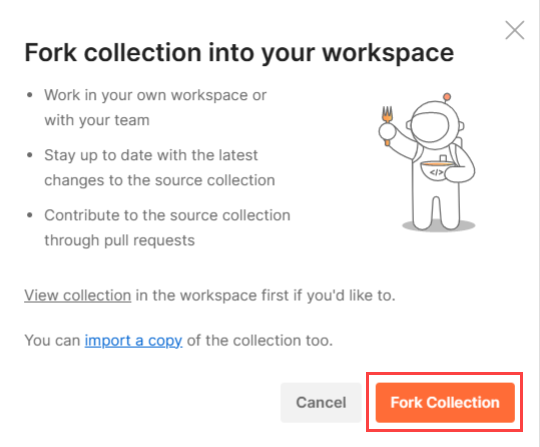
- This opens the Sign In page. You can either enter your login credentials and click Sign in, or sign in using your Google account or via SSO.
- In the resulting Fork collection modal, if needed, enter a Fork label that lets you uniquely identify your collection and select a Workspace.
- Once done, click Fork Collection to fork the Postman collection into your selected workspace.
Under Notifications, check Watch original collection to get notified of any changes that are made to the original collection.
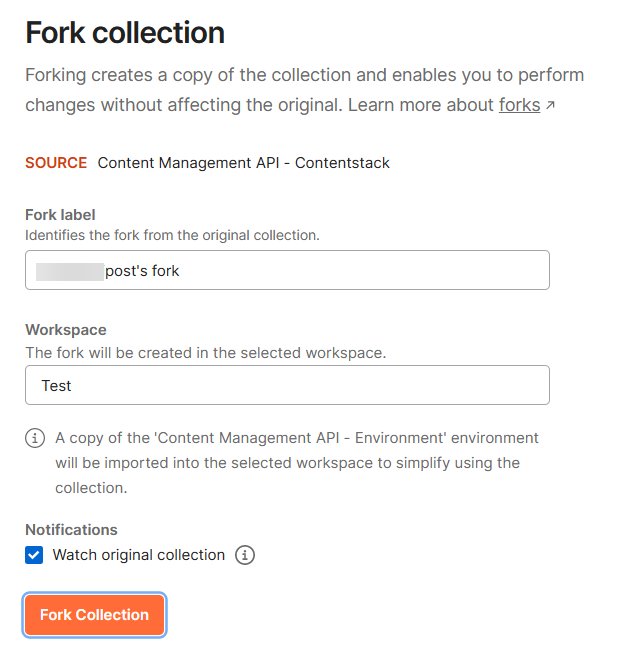
Download Collection from GitHub Page
We have also hosted our Postman collection on GitHub. You can follow the steps mentioned in the Readme file to download and start using it.
You can also choose to watch the latest Postman collection to get notifications of new releases or updates.
To do so, click on the following Watch button and select Watching.
Configure Environment Variables
When you download and install the latest version of the Content Management API (CMA) Postman Collection, you also download and import the respective environment along with the environment variables.
Once your Environment is imported, next you need to set your Contentstack account specific values.
Note: As these environment variables are referenced across multiple API requests, once you set the variables, it becomes a lot more convenient to make repeated use of the Postman Collection.
Some of the important variables that you need to set are as follows:
| Environment Variable | Value |
|---|---|
| base_url | api.contentstack.io |
| api_key | your_stack_api_key |
| authorization | your_management_token |
Note: The Contentstack Postman Collection will require a valid Management token to make API calls. Check out the Authentication section for more details.
If you want to add your own environment variables, you can follow the procedure in the next section.
Add Other Environment Variables
To add any new environment variables for your Postman collection, perform the following steps:
- Identify the environment variables that you want to define.
- In the top right corner of Postman, click on the environment's dropdown and select Content Management API - Environment.
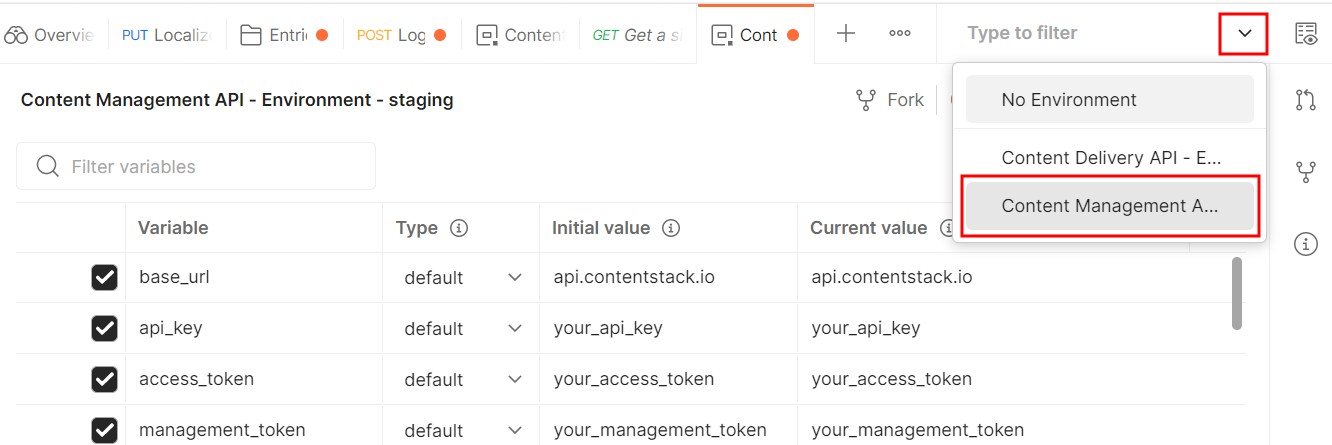
- Click the "eye" icon present in the top right corner of Postman. It opens up in the environment variables modal. Click Edit to make changes in the variables.
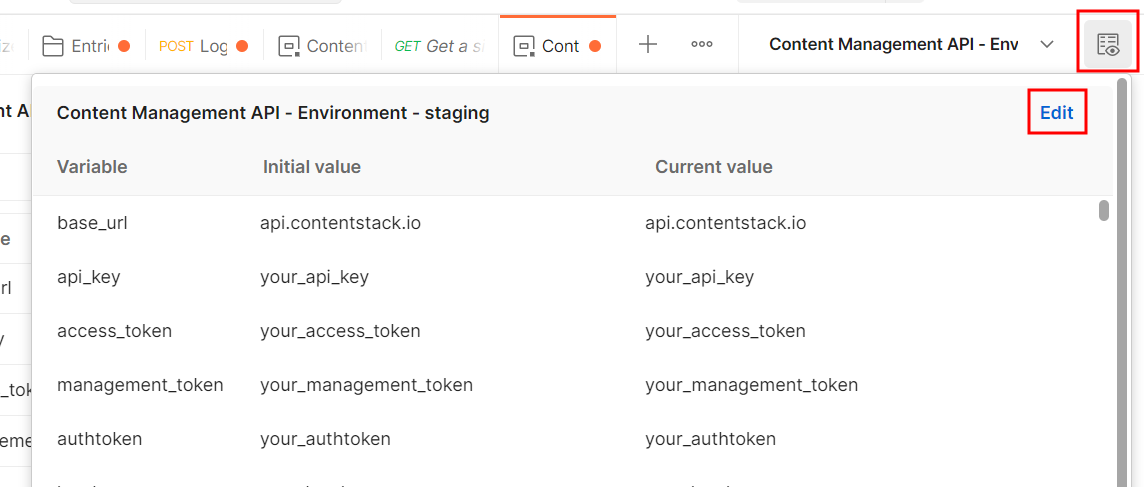
- In the VARIABLE field, enter the name of the environment variable. In the INITIAL VALUE field, enter your Contentstack-account-specific value that will replace the variable when the call is made.
- Once you have defined your variables, click on Save.
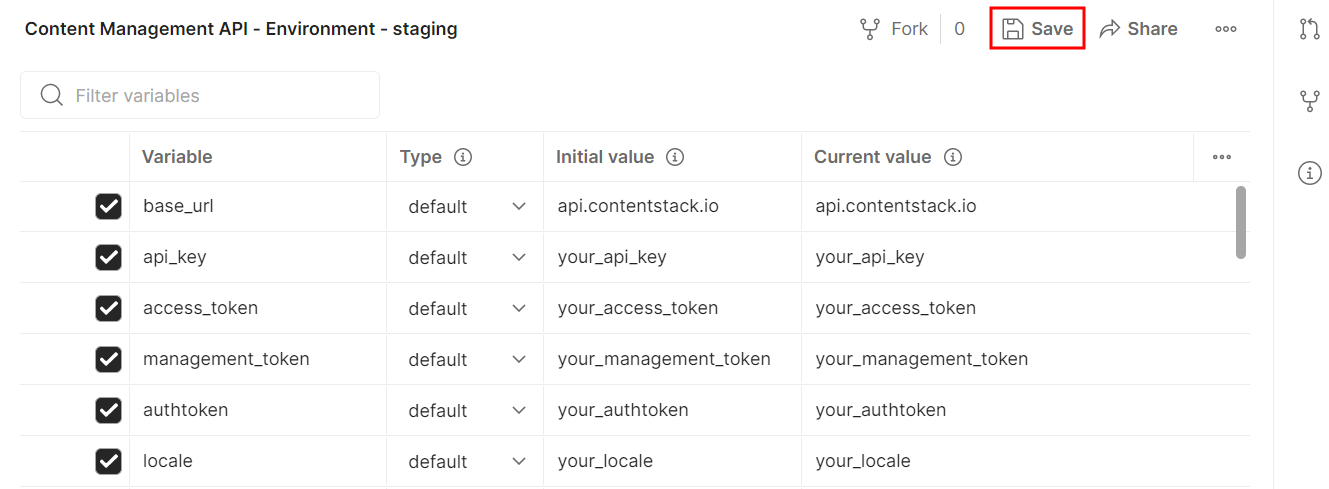
Update Environment Variables
With every new API request added, we update our environment file. So, to get the latest environment variables, you need to download the collection along with the updated environment file again, compare your existing environment with the latest environment, identify and add the new variables to your existing environment.
Next, let’s see how you can run API Requests from your Contentstack Postman collection using your environment.
Make an API Request
With the Contentstack Postman Collection loaded into the Postman app (on the left pane) and the environment created, you can now make API requests to the Contentstack API via Postman.
To make an API request, perform the following steps:
- Select the respective environment, Content Management API-Environment, from the dropdown.
- Select an API Request from the Contentstack Postman Collection. In this example, we will use the Get user request which is a part of the Users folder.
Note: If you want to make changes to your parameters or want to add parameters of your own, you can do it here.
- Next, click on Send at the top right to make the API request.
The API call should return with a response under the Body tab in the bottom half of the screen.
Secure API Keys and Tokens
We strongly advise against storing your API keys and tokens in your collection permanently. If you or someone else shares the collection by mistake, other users will be able to export it along with these keys.
We recommend that you provide your Contentstack account-specific API keys and tokens in your environment or directly to the sample requests.
Users using Authtoken
For users who use authtoken to authenticate their calls, when you make the Log in to your account API Request, your authtoken will be saved in cookies.
If you want to prevent this action, perform the steps given below:
- Click on Cookies on the far right corner.
- In the Cookies modal under the Manage Cookies tab, click the Domains Allowlist at the bottom left.
- Add api.contentstack.io and click Add.
This will allow you to access cookies of this domain in scripts programmatically.
Note: To avoid this situation, we recommend you to use the stack’s Management Token along with the stack API key to make valid Content Management API requests. For more information, refer to Authentication.
Postman Collection Updates
We keep our Postman Collection updated. To get the latest version of our Postman Collection, all you need to do is to download the Postman Collection along with the updated environment again and you are good to go.
You can also choose to watch for the latest Postman Collection updates on our GitHub repository and get notifications of new releases or updates to the repository. The GitHub Readme doc will help you with the steps that you need to follow.





.jpg?format=pjpg&auto=webp)