Astro Sample Website
Warning: This sample website is no longer maintained. It remains available for reference only. If you have questions regarding this, please reach out to our support team, and we will do our best to help!
Astro is an all-in-one web framework for building fast and content-focused websites.
This guide helps you to create a starter marketing website built using the Astro framework with minimal steps. It uses Contentstack’s Node.js Delivery SDK to store and deliver the website content from Contentstack.
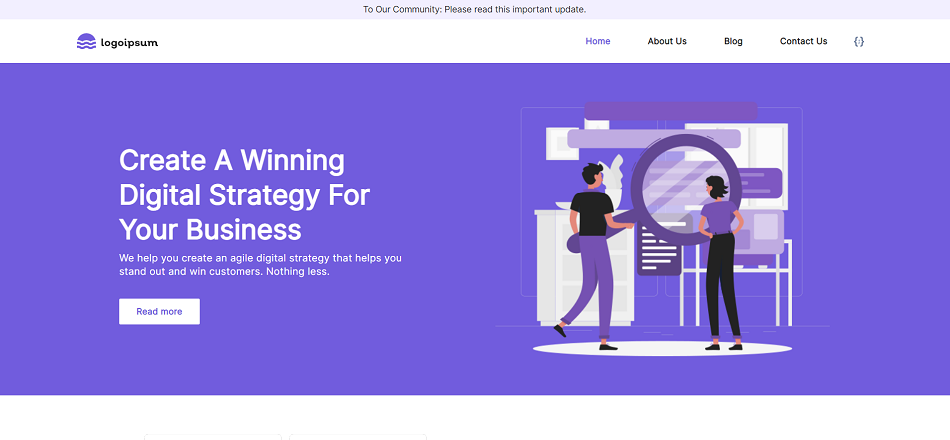
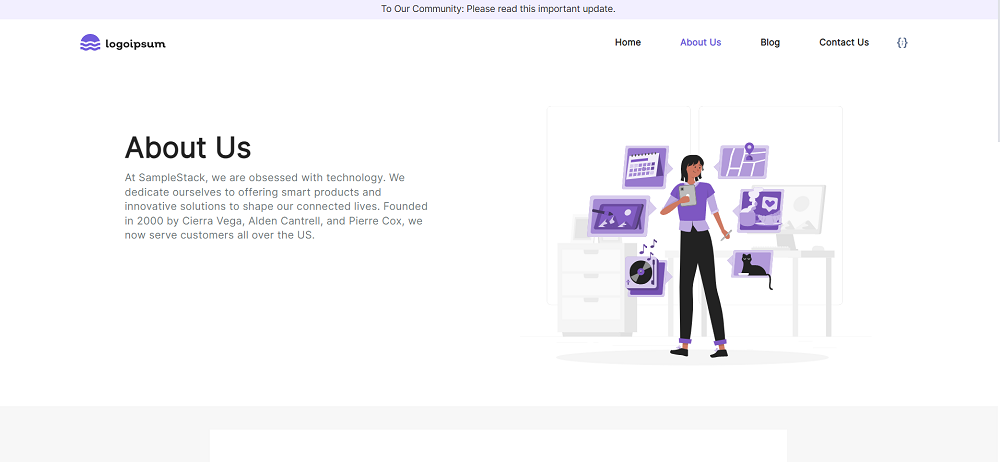
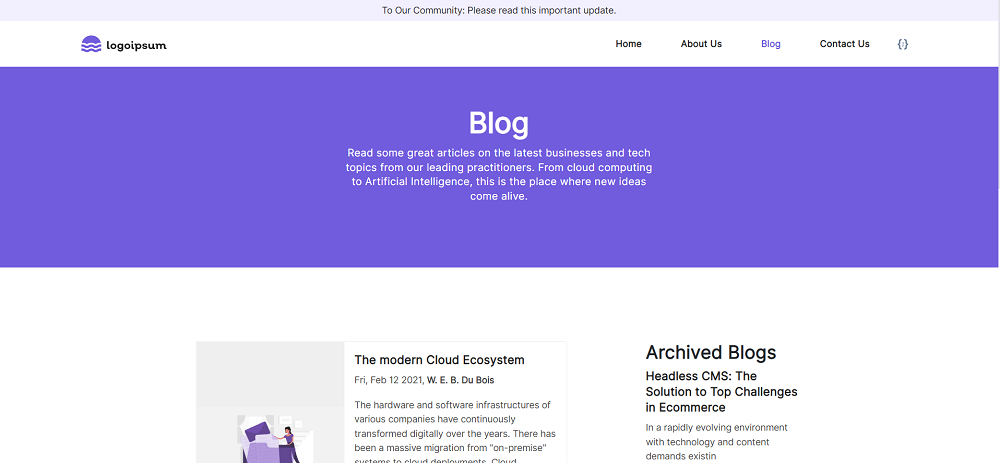
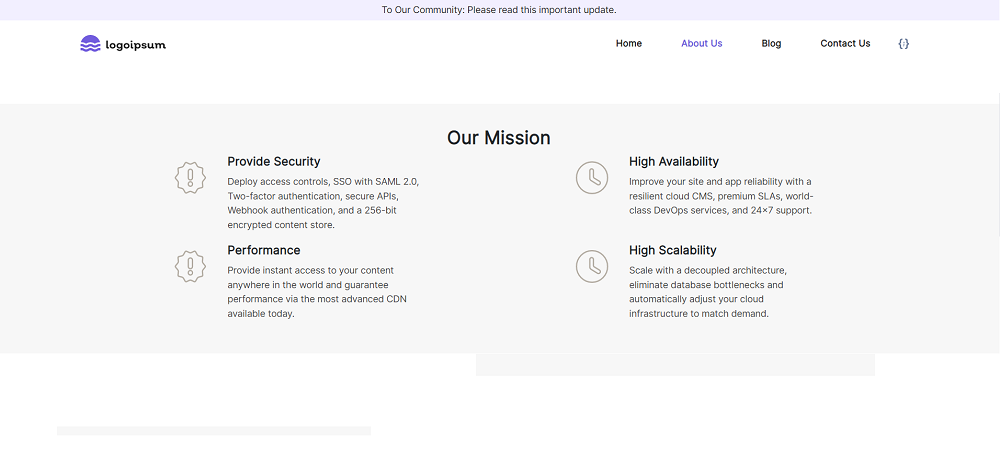
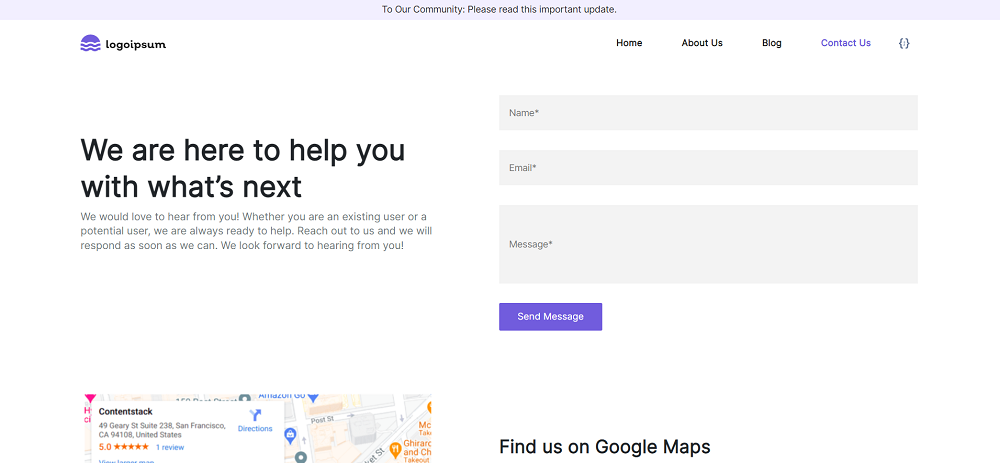
Screenshots
Let’s look at the steps to create a starter website using Astro and Contentstack.
Prerequisites
- Contentstack account
- Node.js version 20 or later
- Contentstack CLI: npm install -g @contentstack/cli
Note: For this tutorial, we have assumed that you are familiar with Contentstack and Astro. If not, please refer to the Contentstack docs and Astro docs for more details.
Supported Features
- Branches: Leverage the Branches feature to manage different versions of your content within Contentstack, allowing for organized development and deployment.
Set Up Your App
Here is an overview of the steps involved in creating our Astro app:
- Set the Region
- Log in to your Account
- Import Content
- Create Delivery Token
- Build and Configure the Website
- Deploy the Website
Set the Region
To use the North America, Europe, Azure North America, Azure Europe, Google North America, or Google Europe endpoint, run the following command in your terminal (command prompt):
csdx config:set:region <<region>>Note:- For North American users, set the region as NA.
- For European users, set the region as EU.
- For Azure North American users, set the region as AZURE-NA.
- For Azure European users, set the region as AZURE-EU.
- For Google North America users, set the region as GCP-NA.
- For Google Europe users, set the region as GCP-EU.
Log in to your Account
To import content to your stack, you need to log in to your Contentstack account via CLI by running the following command in your terminal:
csdx auth:loginThis command requests you to provide your Contentstack’s account credentials (i.e., email and password).
Note: Currently, Contentstack does not support strict SSO for CLI authentication. To access CLI from strict SSO-enabled organizations, go to the Organization Settings and change the SSO strict mode to a user-by-user basis. Once done, you can enable it for certain developers or create a developer account that you can share with developers to access the CLI. For more login details, refer to CLI Authentication and Adding Tokens.
Import Content
The seed command lets you import content to your stack in a few steps. To do so, run the following command in your terminal:
csdx cm:stacks:seed --repo "contentstack/stack-starter-app"This command prompts the following options:
- Organization name: You will get a list of organizations to which you have access. Select the one from the list where your source stack is located or where you want to create a new stack.
Note: Choose an organization where you are an owner or admin.
- Stack preference: Next, you will get an option to create a new stack or use an existing stack.
- If you select New, you must enter the stack name, and the stack creation process will start.
- If you select Existing, you will get a list of stacks to which you have access in the organization. Choose the destination stack where you want to import the content. If the existing stack has some content, it will ask for a confirmation to continue with the same stack.
Additional Resource: Refer to the Stack Roles documentation to learn more about permissions.
Tip: To avoid the chances of any error, we recommend that you select the option of creating a new destination stack. If you import content to an existing stack, ensure that the stack is empty.
Finally, you will get the content imported to your stack.
- Organization name: You will get a list of organizations to which you have access. Select the one from the list where your source stack is located or where you want to create a new stack.
Create Delivery Token
A delivery token lets you fetch published content from an environment.
You can create a delivery token for the development environment to run the website on localhost. Later, you can create tokens for the other environments while deploying your site.
Build and Configure the Website
Fire up your terminal, navigate to your project folder, and run the following command to create a configuration file named .env.local.
cp .env.sample .env.localNote: If you are a Windows user, replace cp with copy in the command given above.
The .env.local file contains all the necessary config parameters. Open it in any code editor or IDE of your choice, provide your stack credentials as shown below, and save the file.
CONTENTSTACK_API_KEY = <api_key_of_your_stack> CONTENTSTACK_DELIVERY_TOKEN = <delivery_token_of_the_environment> CONTENTSTACK_ENVIRONMENT = <environment_name> CONTENTSTACK_REGION = <region> CONTENTSTACK_API_HOST = cdn.contentstack.io # By default branch=main, if a branch is not provided # CONTENTSTACK_BRANCH = <your_branch_name> # By default region=us, if a region is not provided # CONTENTSTACK_REGION = <your_region_name>Note:- The default CONTENTSTACK_API_HOST URL is set to cdn.contentstack.io. You can also add your own Custom Host URL.
- For Europe (EU) region, set the CONTENTSTACK_API_HOST as eu-api.contentstack.com.
- For Azure North American (AZURE-NA) region, set the CONTENTSTACK_API_HOST as azure-na-api.contentstack.com.
- For Azure European (AZURE-EU) region, set the CONTENTSTACK_API_HOST as azure-eu-api.contentstack.com.
- For Google North American (GCP-NA) region, set the CONTENTSTACK_API_HOST as gcp-na-api.contentstack.com.
- For Google European (GCP-EU) region, set the CONTENTSTACK_API_HOST as gcp-eu-api.contentstack.com.
Run the following commands in your terminal:
npm install npm run dev
That’s it!
You can now view the website at http://localhost:3000. Also, you have the stack with all the website content and resources. Try experimenting by creating new entries and publishing them in the development environment. You should be able to see the changes on the website at localhost.
Deploy the Website
The easiest and quickest way to deploy an Astro starter website on production is to use Vercel. You need a Vercel account before you start deploying.




.svg?format=pjpg&auto=webp)
.svg?format=pjpg&auto=webp)
.png?format=pjpg&auto=webp)






.png?format=pjpg&auto=webp)