About Localization Operator
The localization operator in Contentstack's Advanced Search lets you find entries based on their localization status in specific languages. This feature is especially useful for locating entries that are either localized in a particular language or those that are not yet localized but available in their fallback languages.
Tip: Before using the localization operator, get acquainted with Advanced Search queries.
To use the localization operator, log in to your Contentstack account and perform the following steps:
- Navigate to your stack and select the Entries module.
- Click the Advanced Search option next to the search bar.
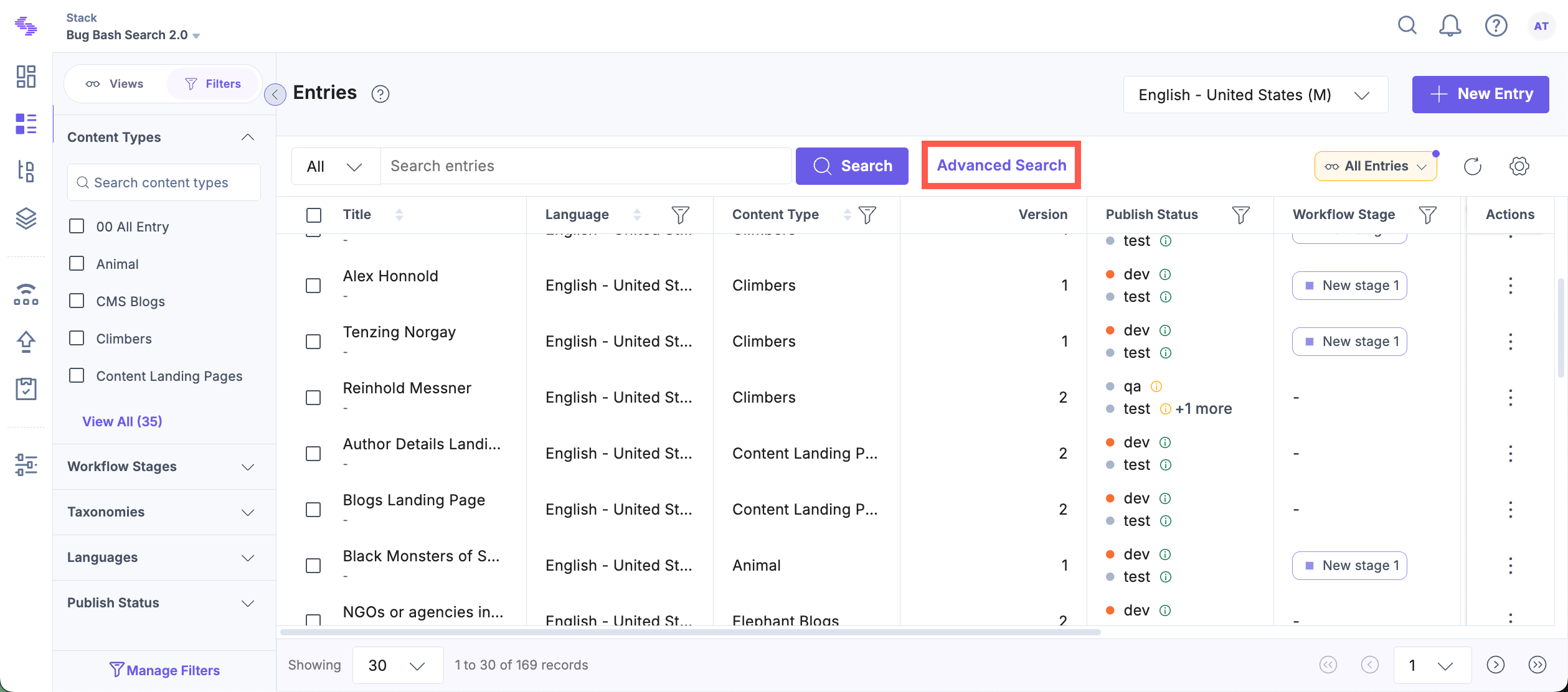
- By default, you will see Match All Conditions, but you can switch to Match Any Conditions if needed.
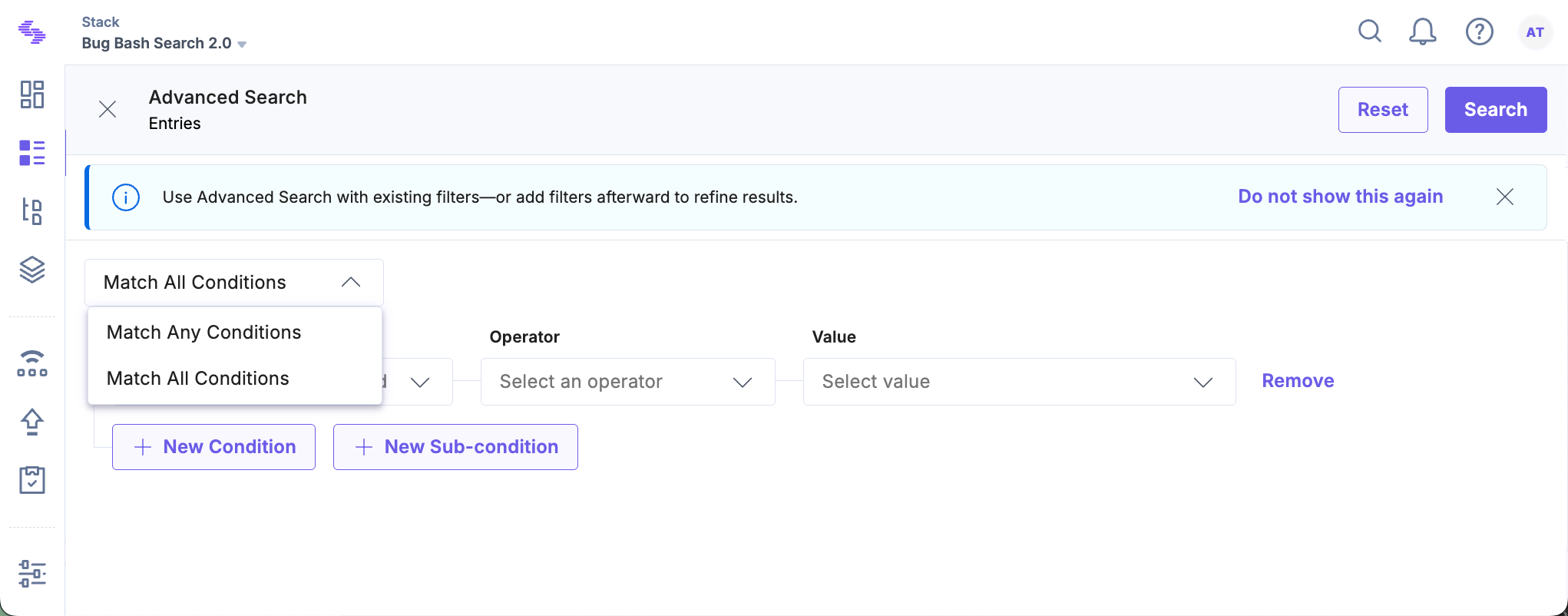
- Select Language from the Content Type or Field dropdown.
- From the Operator dropdown, select Matches to find entries where the language matches a specific value.
- Choose the language you want to search for, such as French.
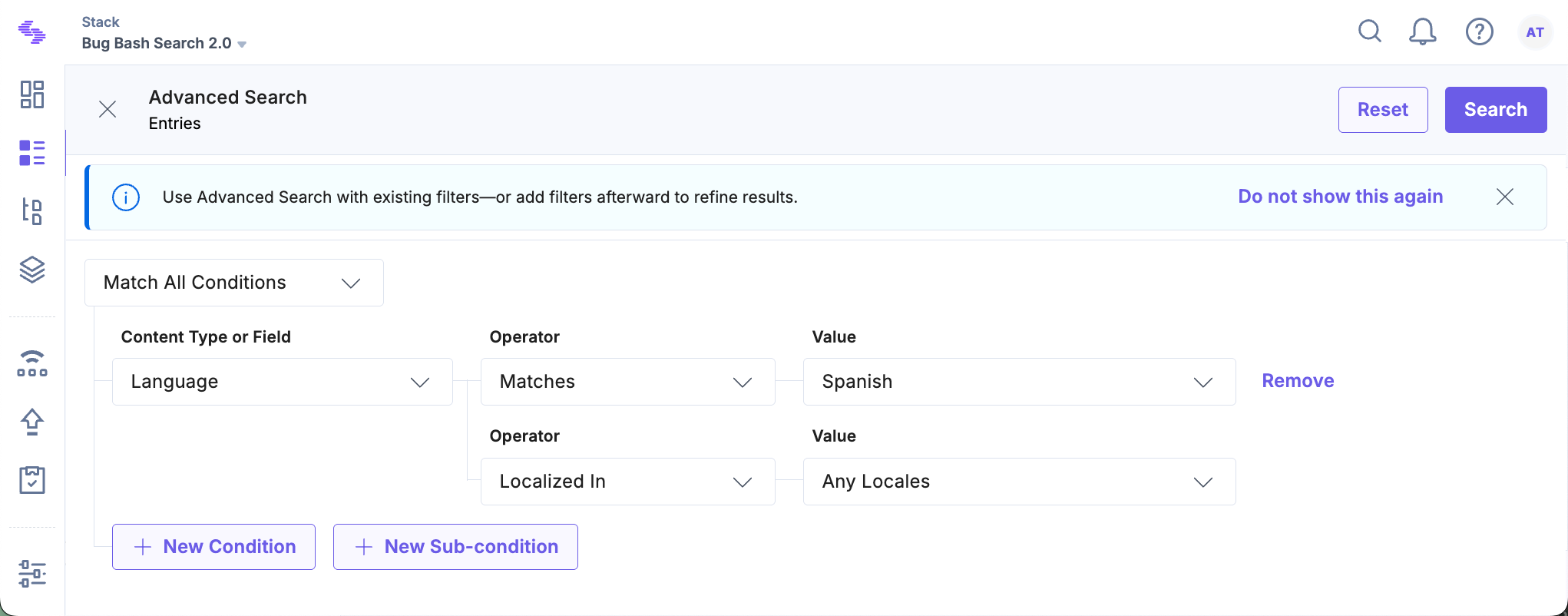
- Choose the operator that fits your needs:
- Localized In: Select this option if you want to find entries that have been localized in a specific language.
- Not Localized In: Select this option to find entries that have not been localized in a specific language but might be available in their fallback languages.
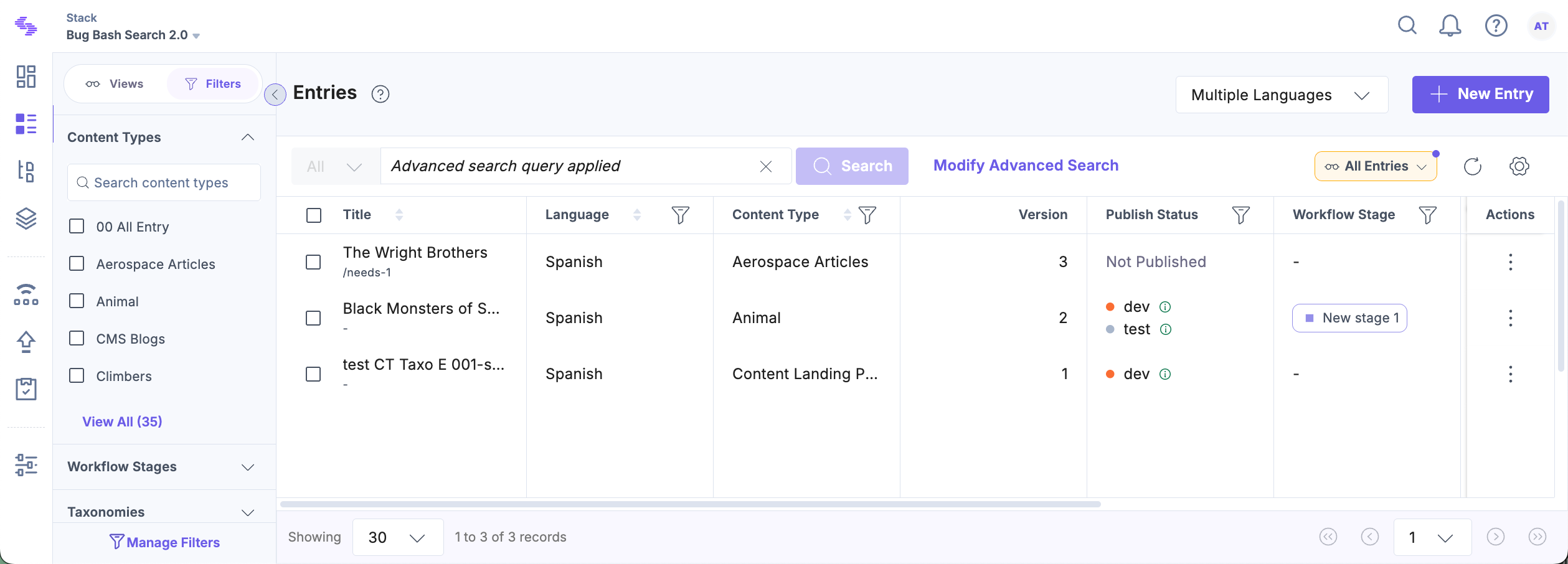
For example, to find entries that have not been localized in French:
- Set the Language field to French.
- Choose Not Localized In from the Operator dropdown.
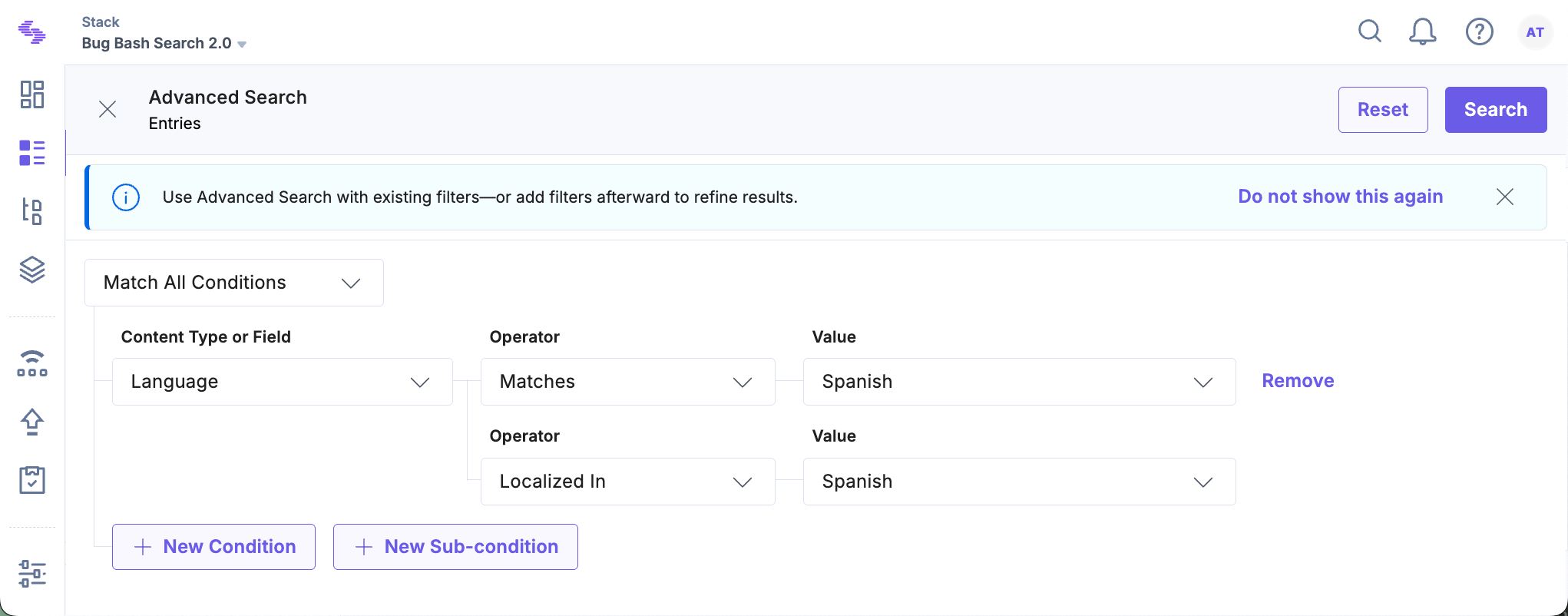
- You can add more criteria or filters as needed to narrow down your search. Once your query is set up, click the Search button to view the results.
- Explore real-world localization examples in our Localization Operator Real-world Scenarios article.
- Refer to the Localization section to understand how languages work in Contentstack.




.svg?format=pjpg&auto=webp)
.svg?format=pjpg&auto=webp)
.png?format=pjpg&auto=webp)






.png?format=pjpg&auto=webp)